The Halogens - Disproportionation Reactions in Halogens (A-Level Chemistry)
Disproportionation Reactions in Halogens
Disproportionation Reactions in Halogens
Reaction of Halogens with Alkalis
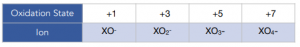
- Halogens can exist in a range of different oxidation states. Apart from halide ions where halogens have an oxidation state of -1, halogens can form compound ions with oxygen with variable oxidation state. These ions are names according to the halogen they form from and end in -ate (i.e.: chlorate, bromate, iodate)
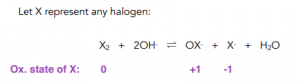
- When a halogen is mixed with a hot alkali a disproportionation reaction takes place. Just as with cold alkalis, halogens will get both reduced and oxidised but the compound ion formed will be different.
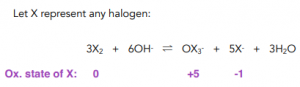
Bleach Formation
- When chlorine gas is mixed with cold, dilute, aqueous sodium hydroxide, sodium chlorate (I) solution is formed. Sodium chlorate (I) solution (NaClO) is also known as bleach that is used to kill bacteria in households. Bleach can also be used in water treatment and to bleach paper or textiles.
- The reaction between chlorine and sodium hydroxide is also a disproportionation reaction. Chlorine undergoes a disproportionation as it is simultaneously reduced from 0 in Cl2 to +1 in NaClO and oxidised to -1 in NaCl.
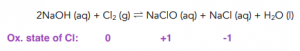
Reaction of Chlorine with Water
- If chlorine is mixed with water, chlorine undergoes a disproportionation reaction. A mixture of both chloride ions and chlorate (I) ions is formed. Chlorine is oxidised from a state of 0 in Cl2 to -1 in Cl-. Chlorine is also reduced from a state of 0 in Cl2 to +1 in ClO-
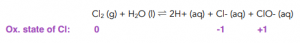
- When present in sunlight, chlorine decomposes water to form chloride and oxygen. Chlorine can decompose water into chloride ions, hydrogen ions and oxygen.

- Chlorine in the form of chlorate (I) ions is used to kill bacteria in water treatment. Chlorine or a compound containing chlorate (I) ions so that people can drink it and swim in it safely.
When deciding if chemicals should be added to water supplies or not, society needs to assess the advantages and disadvantages.
It is worth to note here that we should also appreciate that the benefits to health of water treatment by chlorine outweigh its toxic effects. The advantages and disadvantages of adding chlorine to drinking water is summarised in the table below:

Halogens are a group of non-metal elements found in the periodic table, including fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), and iodine (I). They are known for their high reactivity and ability to form compounds with other elements.
Halogens have a wide range of applications, including use in the production of various chemicals, such as bleach and disinfectants, as well as in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, electronics, and flame retardants.
Disproportionation reactions in halogens are reactions in which a single element is oxidized and reduced simultaneously. For example, in a reaction between two different halogens, such as chlorine and bromine, one halogen will act as an oxidizing agent and the other as a reducing agent, resulting in the formation of two new halogen compounds.
Disproportionation reactions in halogens are important because they demonstrate the highly reactive nature of the halogens and their ability to undergo oxidation and reduction reactions. These reactions also illustrate the concept of redox reactions and help students understand how the halogens can be used in a variety of chemical processes.
To perform a disproportionation reaction in halogens, a halogen is typically mixed with an oxidizing or reducing agent. The reaction is typically carried out in a solution or in a gas phase, and the conditions, such as temperature and pressure, are carefully controlled to ensure that the reaction proceeds as desired.
The products of a typical disproportionation reaction in halogens vary depending on the reactants and conditions of the reaction. However, typically two new halogen compounds are formed, with one acting as an oxidized species and the other as a reduced species.
Disproportionation reactions in halogens have a wide range of real-world applications, including use in the production of chemicals, such as chlorine and hydrogen chloride, as well as in the treatment of wastewater and in the purification of drinking water. These reactions are also used in the synthesis of various compounds, such as pharmaceuticals and industrial chemicals. Understanding the principles of disproportionation reactions in halogens is important for making informed decisions in many industries and applications.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment