Atomic Structure - Atomic and Mass Number (A-Level Chemistry)
Atomic and Mass Number
Atomic and Mass Number
Key Terms
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. Each element has its own atomic number, characteristic of the element and helping you recognise it.
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutron which are found in the nucleus. Electrons have a negligible mass, so we don’t usually count it when working out the mass of an atom.
Nuclear Symbols
It is useful to know what the nuclear symbols are:
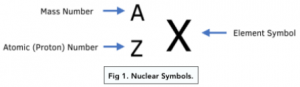
- X is the element symbol
- A is the mass number
- Z is the atomic (proton) number
Calculations
We can perform calculations to determine the number of subatomic particles.
- Mass number = protons + neutrons
- Atomic number = protons
- Number of neutrons = mass number – atomic number
- Number of electrons = number of protons (in an atom)
Ions
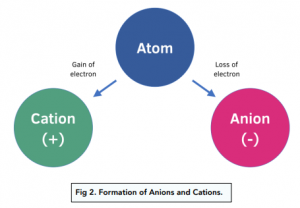
Ions are formed from atoms when electrons are transferred between them:
- A cation a positive ion is formed when an atom has lost electrons, after which it contains less electrons than protons.
- An anion is a negative ion is when an atom gains electrons so it contains more electrons than protons.
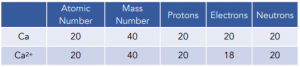
When doing calculations, you need to bear in mind that the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons. However, the atomic and mass numbers stay the same. For example:





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment