Pure Substances & Formulations (GCSE Chemistry)
Pure Substances & Formulations
Pure Substances
- Single elements and compounds are pure. We can call single elements or compounds ‘pure’. They are not mixed with any other substances.
- Pure substances have nothing added to them. As we’ve just mentioned, pure substances are not mixed with any other substances. This means that there are no other substances or compounds added to them.
- Pure substances are in their natural state. Since nothing is added to pure compounds, they are said to be in their natural state. An example of a pure substance could be pure milk.
Melting and Boiling Points
- Melting and boiling points are unique. Pure substances each have a unique specific melting point and boiling point. The temperatures of the melting point and boiling point are specific to the substance.
- Sample purity can be tested. If we know the specific melting or boiling point for a substance, we can test the purity of a sample. If the sample has the same melting or boiling point as the substance, then we can confirm that the substance is pure.
- Impurities can be detected. By using the melting or boiling point of a sample, we can detect impurities. Impurities will change the melting and boiling point of a substance. Impure substances melt and boil over a range of temperatures.
Worked example: Look at the table of data. Which substance is pure?
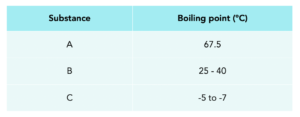
Answer:
A, because it has specific boiling point.
Formulations
- Formulations are useful products. Formulations are designed as useful products. They are created to fulfil a specific purpose.
- Formulations are mixtures of compounds. A formulation is a mixture of compounds. Each compound is carefully measured out, leading to the formulation having specific properties.
- Fuels are formulations. An example of a formulation is fuel. Other examples of formulations include cleaning agents, paints, medicines, alloys, fertilisers and foods.
Identifying Formulations
- Formulations can be identified. By looking at the components of a formulation, we can identify a formulation.
- Amount of compounds can be useful. By looking at the amounts of compounds in a formulation, we can identify different formulations.
- Using ratios to carry out calculations in formulations. We can use the following equation:
Total mass/ total ratio = mass of given substance/ ratio of substance
Worked example: Methylated spirit contains the following substances with their ratio by mass.
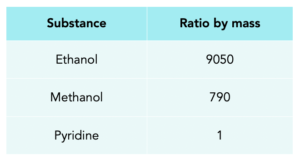
Calculate the amount of methanol in 20 kg of methylated spirit. Give your answer to 3 s.f.
Answer:
1. Calculate the total ratio. Add all the ratios together.
9050+790+1 = 9841
2. Use the equation.
Total mass/ total ratio = mass of given substance/ ratio of substance
3. Rearrange the equation to find mass of methanol.
Mass of substance = total mass/ total ratio x ratio of substance
4. Substitute in values.
Mass of substance = (20/ 9841) x 790 = 1.61 kg
Percentage Purity
The percentage purity can be calculated to determine the percentage of a material which is actually useful.

Worked example: A 15.00g sample of a pharmaceutical drug contains 14.85g of the active drug. Calculate the percentage purity of this drug. (2 marks)
1.Write down the equation for percentage purity.
% Purity = Mass of useful product x 100
——————————
Total mass of product
2. Substitute in the numbers.
% Purity = (14.85/15) x 100
3. Calculate the percentage purity.
% Purity = (14.85/15) x 100
Pure substances in GCSE Chemistry are substances that are made up of only one type of particle, either atoms or molecules. They have a fixed composition and a distinct set of properties.
There are two main types of pure substances in GCSE Chemistry: elements and compounds. Elements are substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances, while compounds are substances that are made up of two or more elements combined chemically.
The properties of pure substances in GCSE Chemistry include their melting point, boiling point, density, conductivity, and solubility. These properties can be used to identify a pure substance and to distinguish it from other substances.
Formulations in GCSE Chemistry are combinations of two or more pure substances that are mixed together to form a new substance with a different set of properties. Formulations can be either homogeneous, meaning that the components are evenly mixed, or heterogeneous, meaning that the components are not evenly mixed.
Examples of formulations in GCSE Chemistry include solutions, suspensions, and colloids. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, while a suspension is a heterogeneous mixture of two or more substances. A colloid is a mixture of two or more substances that is intermediate between a solution and a suspension.
The properties of a formulation in GCSE Chemistry can be predicted by understanding the properties of its component pure substances and the way in which they interact with each other. For example, the solubility of a substance in a solution can be predicted based on the properties of the solvent and the solute.
A mixture in GCSE Chemistry is a combination of two or more pure substances that are not chemically combined, while a formulation is a combination of two or more pure substances that are chemically combined. A mixture retains the individual properties of its component pure substances, while a formulation has a new set of properties that is different from those of its component pure substances.
A homogeneous formulation in GCSE Chemistry is a mixture in which the components are evenly mixed and cannot be easily separated, while a heterogeneous formulation is a mixture in which the components are not evenly mixed and can be easily separated. An example of a homogeneous formulation is a solution, while an example of a heterogeneous formulation is a suspension.
The concentration of a substance in a formulation in GCSE Chemistry can affect its properties. For example, the solubility of a substance in a solution is affected by the temperature and pressure of the solution, as well as the concentration of the solute.
The mole concept in GCSE Chemistry is a unit of measurement used to describe the amount of a substance in a formulation. The mole is defined as the number of particles in a substance that contains Avogadro’s number of particles. The mole is used to calculate the mass of a substance in a formulation and to balance chemical reactions.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment