Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions (GCSE Chemistry)
Components of an Aqueous Solution
Ions in Water
- Electrolytes are aqueous or molten. In order for electrolysis to occur, compound must be dissolved in water, or melted to form a liquid. This means that the ions are free to move around when a current is applied.
- Aqueous electrolytes contain water. When a compound is dissolved in water, the resulting solution has water present. This means that there is both the ionic compound and water molecules in the solution.
- Water splits into ions. Water molecules can split into two ions: hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH–). When joined together, they produce water molecules, H2O.
H2O ⇌ H+ + OH–
Ion Production with Aqueous Electrolytes
When aqueous electrolytes are involved, electrolysis is slightly more complicated.
- Two ions are attracted to the cathode. The hydrogen ion and the metal ion are attracted to the cathode. To decide what substance is made at the cathode, we must use the reactivity series.
- Metal reactivity is compared to hydrogen. If the metal element formed during electrolysis is more reactive than hydrogen, then hydrogen will be produced at the cathode. If the metal element formed is less reactive than hydrogen, then the metal is produced at the cathode.
- Two ions are attracted to the anode. The hydroxide ions and halide ions are attracted to the anode. If both are present, then a halogen is formed. If no halide ions are present, then the hydroxide ions are discharged, and oxygen is formed.
Example of Aqueous Electrolysis
Practice Question 1: Write out the half equations for the electrolysis of copper sulfate.
1.Write out all the ions. For these questions, it is easier to write out all the ions before you start the ionic equation.
Cu2+, SO42-, H+, OH–
2. Look at the cathode. We can form either Copper or Hydrogen. Copper is less reactive than hydrogen on the reactivity series, so Copper is formed, coating the electrode.
Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
3. Look at the anode. No halide ions are present, so hydroxide ions are discharged, forming water and oxygen.
4OH– → O2 + 2H2O + 4e–
Practice Question 2: Write out the half equations for the electrolysis of sodium chloride.
1.Write out all the ions.
Na+, Cl–, H+, OH–
2. Look at the cathode. Either sodium or hydrogen can be formed. Since sodium is more reactive than hydrogen, hydrogen is made.
2H+ + 2e– → H2
3. Look at the anode. Anode: either chlorine or hydroxide ions, however halides take precedence, so chlorine is made.
2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Electrolysis with Inert Electrodes
Coming Up with A Hypothesis
For exams, you need to be able to investigate what happens when we electrolyse inert solutions with aqueous electrodes.
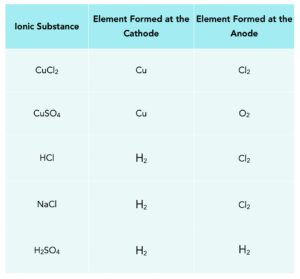
This table shows some of the elements formed at the anode and cathode when ionic compounds are electrolysed using inert electrodes.
FAQs
Electrolysis of aqueous solutions is a process in which an electrical current is passed through an aqueous (water-based) solution to cause chemical reactions. This process splits the ions in the solution into individual atoms, allowing them to gain or lose electrons.
An aqueous solution is a solution in which water is the solvent. It can be divided into two parts:
Solvent: The solvent is the component of the solution that is present in the greatest amount. In an aqueous solution, water is the solvent. Water is a polar molecule, which means that it has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end. This polarity makes water an excellent solvent for ionic compounds and polar molecules, as it can surround and separate the ions or molecules, allowing them to dissolve.
Solute: The solute is the component of the solution that is present in a smaller amount than the solvent. It is the component that is being dissolved in the solvent. In an aqueous solution, the solute can be any substance that is soluble in water, such as salts, acids, bases, sugars, and many other compounds.
The properties of an aqueous solution are determined by the properties of both the solvent and the solute. For example, the concentration, pH, and conductivity of an aqueous solution are all affected by the properties of the solute and the solvent.
Electrolysis with inert electrodes is a process of electrolysis in which inert (non-reactive) electrodes, such as platinum or graphite, are used to carry out the electrolysis reaction. In this process, an electric current is passed through an electrolytic cell containing an aqueous solution or a molten electrolyte, causing a chemical reaction to occur at the electrodes.
The inert electrodes are used to avoid any unwanted chemical reactions with the electrodes themselves. This is important because some electrodes can react with the electrolyte or the products of electrolysis, leading to unwanted side reactions that can interfere with the desired process.
During electrolysis with inert electrodes, the positive electrode (anode) attracts negatively charged ions, which lose electrons to become neutral atoms or molecules. This process is known as oxidation. At the same time, the negative electrode (cathode) attracts positively charged ions, which gain electrons to become neutral atoms or molecules. This process is known as reduction.
Electrolysis with inert electrodes is used in a wide range of industrial processes, such as the production of chlorine gas, sodium hydroxide, and aluminum metal.
Electrolysis of aqueous solutions is an important topic in GCSE Chemistry because it demonstrates the concept of ionic compounds, how they behave in solution, and how they can be separated through chemical reactions. It also highlights the role of electricity in chemical reactions and provides a practical application of the knowledge and skills learned in the GCSE Chemistry course.
During the electrolysis of aqueous solutions, an electrical current is passed through the solution, causing the ions in the solution to gain or lose electrons. This results in chemical reactions, such as the formation of gas or the deposition of metal, at the electrodes. The type of reaction that occurs depends on the properties of the ions in the solution and the type of electrode used.
An electrode in electrolysis of aqueous solutions is a conductor that is used to pass an electrical current into the solution. There are two types of electrodes in electrolysis: the anode, which is the electrode that attracts positively charged ions, and the cathode, which is the electrode that attracts negatively charged ions.
To set up an electrolysis of aqueous solutions experiment, you need an aqueous solution, two electrodes (an anode and a cathode), a power source, and a way to measure the amount of products produced. The solution is placed between the two electrodes and an electrical current is passed through the solution. The reactions that occur at the electrodes are observed and the amount of products produced is measured.
Electrolysis of aqueous solutions can be influenced by a variety of factors. Here are some of the main factors that can affect the process:
Nature of the electrolyte: The type of electrolyte used can greatly affect the electrolysis process. Strong electrolytes, such as sodium chloride or sulfuric acid, dissociate almost completely into ions in solution, while weak electrolytes, such as acetic acid, only partially dissociate. This can affect the conductivity of the solution and the ease of electrolysis.
Concentration of the electrolyte: The concentration of the electrolyte can also impact the conductivity of the solution and therefore the ease of electrolysis. A more concentrated solution will generally be more conductive and therefore easier to electrolyze.
Nature of the electrodes: The nature of the electrodes used can also impact the electrolysis process. The electrode materials can affect the rate of electron transfer and therefore the rate of electrolysis. For example, using inert electrodes such as platinum or graphite can reduce unwanted side reactions, while using reactive electrodes such as copper or iron can result in the formation of undesired products.
pH of the solution: The pH of the solution can affect the behavior of the electrolyte and the products of electrolysis. In acidic solutions, hydrogen ions (H+) are more likely to be reduced, while in alkaline solutions, hydroxide ions (OH-) are more likely to be oxidized.
Temperature: The temperature of the solution can affect the rate of reaction and therefore the rate of electrolysis. Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of reaction, while lower temperatures can slow it down.
Presence of impurities: The presence of impurities in the solution can also affect the electrolysis process. Impurities can react with the electrodes or the products of electrolysis, leading to unwanted side reactions and affecting the overall efficiency of the process.
The products of electrolysis of aqueous solutions depend on the properties of the ions in the solution and the type of electrode used. Common products include the formation of hydrogen gas at the cathode and oxygen gas at the anode, or the deposition of metal at the cathode.
The concentration of aqueous solutions can affect the electrolysis process by changing the number of ions in the solution. A higher concentration of ions in the solution will result in a faster rate of reaction, as there are more ions available to gain or lose electrons.
Electrolysis of aqueous solutions has practical applications in industry, such as the extraction of metal from ore and the production of hydrogen gas for use as a fuel. The process is also used in electroplating, which is the process of depositing a metal onto a surface to provide a thin layer of metal for protection or decoration.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment