Carbonates, Halides & Sulphates (GCSE Chemistry)
Carbonates, Halides & Sulphates
Tests For Carbonates
- Dilute acids identify carbonates. In the test to identify carbonates, dilute acids are used. Only a couple of drops need to be used in order to identify these carbonates.
- Carbon dioxide is produced. When dilute acid is added to a carbonate, carbon dioxide is one of the products of the reaction. The other two products are a salt and water.
- We can use the test for carbon dioxide. As we saw earlier, carbon dioxide can be detected using limewater (calcium hydroxide) to create a cloudy solution.
- Carbon dioxide confirms the presence of a metal carbonate. If carbon dioxide is present at the end of the reaction, it confirms that a carbonate was present at the start of the reaction.
Tests For Halides
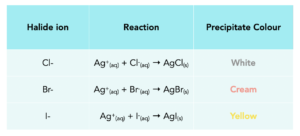
- Silver nitrate solution identifies halide ions. In the test to identify halide ions, silver nitrate solution is used. This is used in the presence of dilute nitric acid.
- Coloured precipitates are formed. When the halide ions react with silver ions, coloured precipitates are formed. We can see the different colours and their reactions in the table below.
Tests for Sulphates
- Barium chloride and dilute hydrochloric acid identify sulphate ions. In the test to identify sulphate ions, barium chloride and dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) are used. HCl is added first, followed by barium chloride.
- A white precipitate is formed. When sulphate ions react with barium ions, a white precipitate is formed. The HCl is used to remove any carbonate ion traces.
Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4(s)
Required Practical 7: Ion Tests
As we have seen throughout this section, there are various tests that can be conducted to identify unknown ions in compounds.
For exams, you are expected to be able to carry out the tests mentioned in this chapter and identify the cations and anions produced.
Worked example: A substance is split into two samples. One part is reacted with acidified silver nitrate and the other with acidified sodium hydroxide. Predict the observations, if the substance is copper (II) iodide.
Answer: Iodide ions will produce a yellow precipitate in acidified silver nitrate; copper(II) ions will produce a blue precipitate in sodium hydroxide solution.
FAQs
Carbonates are chemical compounds that contain a carbonate ion (CO32-) combined with a metal ion. Examples of carbonates include calcium carbonate (CaCO3), which is found in limestone and is used in the construction industry, and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), which is used in detergents and cleaning products.
Halides are chemical compounds that contain a halogen ion (such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine) combined with a metal ion. Examples of halides include sodium chloride (NaCl), which is common table salt, and calcium chloride (CaCl2), which is used as a de-icing agent.
Sulphates are chemical compounds that contain a sulphate ion (SO42-) combined with a metal ion. Examples of sulphates include copper sulphate (CuSO4), which is used in agriculture as a fungicide, and magnesium sulphate (MgSO4), which is used as a fertilizer and in the treatment of eclampsia during pregnancy.
The main difference between carbonates, halides, and sulphates is the type of ion that is combined with a metal ion. Carbonates contain a carbonate ion, halides contain a halogen ion, and sulphates contain a sulphate ion. Each type of compound has its own unique properties and uses.
Carbonates are typically basic (alkaline) compounds, meaning they will react with acids to produce a salt and carbon dioxide gas. They are also generally insoluble in water, except for those of the alkali metals (such as sodium and potassium).
Halides are typically soluble in water and form salts when reacted with acids. They are also generally good conductors of electricity in their solid state, although some halides such as iodine are poor conductors.
Sulphates are typically soluble in water and form salts when reacted with acids. They are also often used as fertilizer in agriculture and in industry for processes such as paper production and dyeing.
Carbonates are used in construction, in the production of glass, and as a source of calcium for animal feed. Halides are used in the production of table salt, in water treatment, and as a de-icing agent. Sulphates are used as fertilizer in agriculture, in the production of paper, and as a component of certain medicinal products.
These questions and answers can help students understand the differences and properties of carbonates, halides, and sulphates and prepare them for their GCSE chemistry exams.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment