Acids, Bases & pH (GCSE Chemistry)
Acids, Bases & pH
Aqueous Solutions
Acids and Bases
- Acids produce hydrogen ions. Acids, which have a pH below 7, will produce hydrogen ions (H+) when placed in aqueous solutions. This means they are proton donors.
- Alkalis produce hydroxide ions. Alkalis, which are soluble bases, have a pH above 7. When placed into aqueous solution, they produce hydroxide ions (OH-), by accepting a hydrogen ion. This means they are proton acceptors.
The pH Scale
- The pH scale is used as a measurement. We can use the pH scale to tell how acidic or alkaline a solution is. The scale goes from 0 to 14, where 0 is very acidic and 14 is very alkaline.
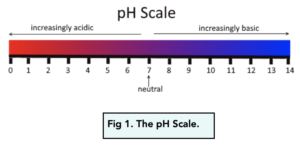
- The pH scale is logarithmic. As hydrogen ion concentration in a solution increases by a factor of 10, the pH of a solution decreases by 1.
Using the pH Scale
- A pH of 7 is neutral. If a solution has a pH of 7, then it is said to be neutral. This means that it is neither acidic nor alkaline. An example of a neutral solution is pure water.
- A pH below 7 is acidic. If a solution has a pH below 7, then it is said to be acidic. Two examples of acidic solutions are vinegar and lemon juice.
- A pH above 7 is alkaline. If a solution has a pH above 7, then it is said to be alkaline. Two examples of acidic solutions are soap powder and washing up liquid.
- Alkalis are soluble bases. As mentioned previously, alkalis are bases that dissolve in water. When aqueous, alkalis form hydroxide ions (OH-). Like bases, alkalis also have a pH above 7.
Measuring pH
Universal Indicator
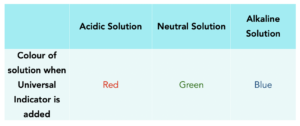
- Indicators measure pH. We can use indicators to measure the pH of a solution. Indicators are dyes and when they are placed into a solution, they will change colour. The colour will depend on the pH of the solution.
- Universal Indicator is a common indicator. Universal Indicator (sometimes written as UI) is the the one that you will come across most often. This is a wide range indicator, since it turns multiple colours depending on the pH of a solution. The colours are shown in the table below.
- pH probes also measure pH. The pH probe measures pH electronically giving a numerical value between 0 and 14. The pH probe is more accurate than using indicator, since it provides a numerical value.
Neutralisation Reactions
- Acids can react with alkalis. When acids react with alkalis to form a salt and water, this is called a neutralisation reaction.
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
E.g. H2SO4 + Mg(OH)2 → MgSO4 + 2H2O
- Water is formed as a product. When acids react with alkalis, the H+ ions from the acids react with the OH- ions from the alkali to form water. This can be seen through an ionic equation.
H+(aq) + OH –(aq) → H2O(aq)
- The products are neutral. The products of a neutralisation reaction (a salt and water) have an overall pH of 7, meaning that they are neutral. If you use universal indicator to show the end of the neutralisation reaction, the solution will turn green.
Classifying Oxides
Acidic and Basic Oxides
- Oxides can be classified as either acidic or basic. We can classify oxides based on their metallic or non-metallic character, which can affect their acidic or alkaline behaviour.
- Acidic oxides are formed from non-metals. When a non-metal reacts with oxygen, an acidic oxide is formed. These can react with bases in a neutralisation reaction to form a salt and water.
- Acidic oxides form an acidic solution. When we dissolve an acidic oxide in water, an acidic solution is produced which will have a low pH.
- Basic oxides are formed from metals. When a metal reacts with oxygen, a basic oxide or hydroxide is formed. These can react with acids in a neutralisation reaction to form a salt and water.
- Basic oxides form a basic solution. When we dissolve a basic oxide in water, a basic solution is produced which will have a high pH.
Neutral and Amphoteric Oxides
- Some oxides are neutral. If an oxide does not react with either an acid or base, we can say it is neutral.
- Some oxides are amphoteric. If an oxide reacts with base an acid and a base, we can say it is amphoteric. Again a neutralisation reaction will occur, so a salt and water will be formed.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment