Group 7: Reactions & Displacement (GCSE Chemistry)
Group 7: Reactions & Displacement
Halogens – Reactions with Non-Metals
Halogens also form covalent bonds with other non-metals to form a molecule. Lets work through an example, below is a generic formula that represents the halogens (X) reacting with hydrogen:
H2 (g) + X2 (g) → 2 HX (g)
When this reaction occurs a hydrogen halide is formed which is gaseous at room temperature. When dissolved in water this forms an acidic solution.
Halogens – Reactions with Metals
The halogens react with metals to form salts. When these salts are dissolved in water they form colourless solutions. Below is a generic formula that represents the halogens (X) reacting with sodium:
2 Na (s) + X2 (g) → 2 NaX (s)
When a halogen reacts with a metal, the metal atom loses an electron forming a positively charged ion. That lost electron is then taken up by the halogen atom, this forms a negatively charged ion. The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other; this is known as ionic bonding.
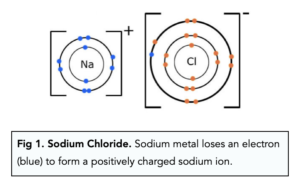
The electron (blue) is then taken up by chlorine to form a negatively charged chloride ion.
2 Na (s) + Cl2 (g) → 2 NaCl (s)
Halogens – Displacement Reaction
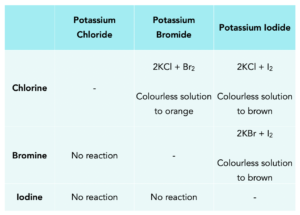
A displacement reaction is when more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halogen from a solution of its salt. All these reactions occur in solution and all the salts when dissolved in water are colourless. Let’s work through some examples.
1. Chlorine solution reacting with potassium bromide
2 KBr (aq) + Cl2 (aq) → 2 KCl (aq) + Br2 (aq)
Chlorine is the more reactive halogen and it will displace bromine from potassium bromide. The aqueous bromine will turn the solution from colourless to yellow-orange.
2. Bromine solution reacting with potassium chloride
2 KCl (aq) + Br2 (aq) → NO REACTION
Chlorine is the more reactive halogen and will not be displaced by bromine. Therefore no reaction will occur and the solution will remain colourless.
Below is a summary of all the displacement reactions you need to know, make sure you learn how to write a balanced equation for all these reactions and observations.
Group 7 in GCSE chemistry refers to the halogens, a group of elements that include fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine.
Group 7 elements are important in GCSE chemistry because they demonstrate common properties and reactivity patterns that can be used to understand and predict chemical reactions.
A displacement reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which one element is replaced by another element in a compound. This occurs when a more reactive element replaces a less reactive element.
The reactivity series in GCSE chemistry is a list of elements ordered from most reactive to least reactive. It is used to predict the outcome of displacement reactions.
Some common examples of displacement reactions in group 7 elements include the reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate to form silver chloride and sodium nitrate, and the reaction between copper and silver nitrate to form copper nitrate and silver.
In a reaction between a metal and a halogen, the metal displaces the halogen to form a metal halide, which is a salt.
The products of a displacement reaction can be determined by using the reactivity series and predicting which element will displace the other.
Displacement reactions occur because elements in a compound have different electronegativities, and the more electronegative element will displace the less electronegative element.
No, a displacement reaction can only occur between a metal and a non-metal.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment