Carboxylic Acids (GCSE Chemistry)
Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic Acids
- ‘COOH’ is the functional group of alcohols. Carboxylic acids have a functional group made up of a C=O bond and C-OH bond on the same carbon, which is simplified to COOH.
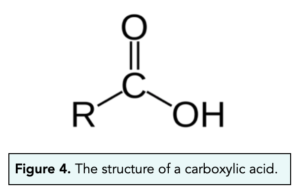
- Carboxylic acids can be named. As we have seen with alkanes, alkenes and alcohols, carboxylic acids can also be named. The first four alcohols in the homologous series are called methanoic acid, ethanoic acid, propanoic acid, butanoic acid.
Representing Carboxylic Acids
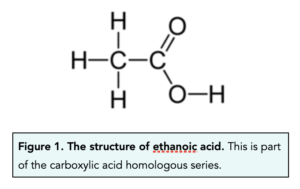
- Carboxylic acids can be represented. We can represent carboxylic acids very easily, by using the number of carbons each molecule contains. Ethanoic acid can be represented as CH3COOH.
- Carboxylic acids can be drawn out. We can also represent carboxylic acids using their displayed formulae. For example, the displayed formulae of ethanoic acid is shown below.
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
- Carboxylic acids undergo various reactions. For exams, you need to know about the reactions of carboxylic acids with carbonates, water and alcohols.
Carboxylic Acids and Carbonates
- Carboxylic acids react with metal carbonates. Like other acids, carboxylic acids can react with metal carbonates.
- Three products are formed. When carboxylic acids react with metal carbonates, salt, water and carbon dioxide are produced. The suffix ‘-anoate’ can be used to name the salts formed.
Propanoic acid + magnesium carbonate ⟶ magnesium propanoate + water + carbon dioxide
Carboxylic Acids and Water
- Carboxylic acids are soluble in water. When carboxylic acids are placed in water, they dissolve. This means that they are soluble.
- H+ ions are formed. When a carboxylic acid dissolves in water, they form free H+ ions. This means that they have ionised. The pH of the solution is decreased, making it weakly acidic.
Weak Acids
- Carboxylic acids ionise in water. As previously mentioned, carboxylic acids can ionise in water. They release H+ ions to form an acidic solution.
- The ionisation is only partial. The ionisation of carboxylic acids in water is only partial ionisation. This means that not all of the H+ ions are released. We use the reversible sign “ ⇌ “ to show that partial ionisation takes place. For example with ethanoic acid, the reaction is written as:
CH3COOH(l) ⇌ CH3COO–(aq) + H+(aq)
- Carboxylic acids are weak acids. Due to this partial ionisation, carboxylic acids are known as weak acids. Their pH is lower than a neutral solution such as water, but higher than a strong acid such as hydrochloric acid.
Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols
- Carboxylic acids react with alcohols. Carboxylic acids can react with alcohols in the presence of a catalyst. They react together to form an ester.
- Concentrated sulphuric acid can be a catalyst. In the reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohols, concentrated sulphuric acid can be the catalyst. As with all catalysts, the sulphuric acid will remain unchanged at the end of the reaction.
Vinegar
Vinegar is an aqueous solution containing ethanoic acid.
It is formed in the reaction between ethanol and oxygen. When a bottle of wine is opened, bacteria uses oxygen from the air to oxidise the ethanol in the wine. This is known as microbial oxidation.
FAQs
Carboxylic acids are a type of organic acid that contains a carboxyl (-COOH) functional group. They are found in many natural substances, such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products.
Carboxylic acids are named by replacing the suffix -e in the alkane name with the suffix -oic acid. For example, the carboxylic acid with the formula CH3COOH is named acetic acid.
Carboxylic acids are typically liquids with a strong, pungent odor. They have a higher boiling point compared to similar-sized alkanes due to the presence of the polar -COOH functional group. Carboxylic acids are also soluble in water due to their polar nature.
Carboxylic acids react with bases to form a salt and water. This reaction is known as a neutralization reaction and occurs because the acidic hydrogen in the carboxylic acid can be replaced by a metal ion from the base. The general equation for this reaction is RCOOH + MOH → RCOOM + H2O, where R represents an alkyl group, M represents a metal ion, and OH represents a hydroxide ion.
Carboxylic acids can react with alcohols to form esters. This reaction, called an esterification reaction, involves the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic acid and its replacement with an alcohol molecule. The general equation for this reaction is RCOOH + R’OH → RCOOR’ + H2O, where R and R’ represent alkyl groups.
Carboxylic acids have a wide range of uses, including as solvents, flavorings, fragrances, and preservatives. They are also used in the production of plastics, resins, and pharmaceuticals. One of the most well-known carboxylic acids is acetic acid, which is used in the production of vinegar.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment