Reactions of Alkenes (GCSE Chemistry)
Reactions of Alkenes
Reactions of Alkenes
Functional Group of Alkenes
- Hydrocarbons have functional groups. Functional groups are the atoms that help to determine the reactivity of a molecule.
- Alkenes have a functional group. The functional group of an alkene is the C=C bond.
Alkenes and Oxygen
- Alkenes can undergo complete combustion. When alkenes react with oxygen, they undergo combustion reactions. They undergo complete combustion, forming water and carbon dioxide.
- Alkenes can undergo incomplete combustion. When burnt in air, alkenes undergo incomplete combustion. They form carbon, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, water and air.
- Burning alkenes in air produces a smoky flame. When alkenes undergo incomplete combustion in the air, a smoky flame is formed. This is due to the production of carbon in the reaction.
Worked example: Write a balanced equation for the incomplete combustion of ethene if carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide are the only products containing carbon.
Answer:
1.State the products of combustion of hydrocarbons. In this case, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and water are formed.
2. Fill in the formulae. Now that we have the products, we can write the symbol equation with the formula for ethene.
C2H4 + O2 ⟶ CO2 + + CO + H2O
3. Balance the equation. On the left-hand side we have 2 carbons, and we have 2 carbons on the right- hand side.
C2H4 + O2 ⟶ CO2 + CO + H2O
On the left, we now have 4 hydrogen atoms. This needs 2 water molecules to balance.
C2H4 + O2 ⟶ CO2 + CO + 2H2O
On the right-hand side, there are 5 oxygen atoms. We need to put 2.5 in front of the oxygen atoms on the left-hand side, but we don’t use decimals in equations, Therefore, we multiply everything by 2 to balance the equation.
2C2H4 + 5O2 ⟶ 2CO2 + 2CO + 4H2O
Addition Reaction of Alkenes
- Alkenes undergo addition reactions. When alkenes react with certain compounds, they undergo addition reactions. This occurs with hydrogen, water and halogens.
- The C=C bond opens. When alkenes undergo an addition reaction, the C=C bond opens. The opening of this bond leads to a single bond between the carbon atoms (C-C), and a ‘free’ bond for another atom to be added.
Alkenes and Hydrogen
- Hydrogen can be added to alkenes. When hydrogen reacts with an alkene, the C=C bond opens. This forms an alkane, with a single bond between the carbon atoms.
- The reaction is known as hydrogenation. Due to hydrogen reacting with the alkene to form an alkane, this is known as a hydrogenation reaction.
- Conditions for this reaction: The reaction with ethene take place with a nickel catalyst at 150 °C
Worked example: Draw structural diagrams of the reactants and products in the reaction of ethene with hydrogen.
Answer:
1.Draw the structural diagrams of the reactants.
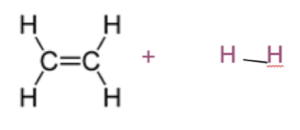
2. Decide how the reactants add across the double bond. Look at both reactants. The double bond will open up and each hydrogen will add to each carbon atom respectively.
3. Draw the product molecule.
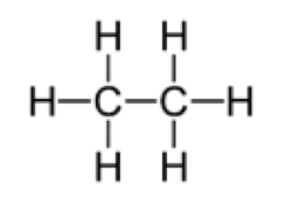
The product is ethane.
Alkenes and Water
- Steam can be added to alkenes. When steam reacts with an alkene, the C=C bond opens. This forms an alcohol, with a single bond between the carbon atoms.
- The water molecule will separate. When the reaction occurs, the water molecule separates into (H) and (OH).
- A catalyst is required for this reaction. When an alkene reacts with steam, a catalyst is required for the reaction to happen.
- Ethanol can be formed from this reaction. Using this method, if ethene (an alkene) is added to steam, ethanol (an alcohol) can be formed. In fact, this method is an industrial way of making ethanol.
- Conditions for the reaction. A phosphoric acid catalyst is used in this reaction. The reaction takes place at 300°C and 60 atmospheres pressure.
Worked example: Draw the product formed when ethene is added to water.
Answer: Part of the water molecule (O-H) will form a bond with one of the carbon atoms and the other part (H) will form a bond with the other carbon atom.
Open up the double bond and add each part to the respective carbon atom.
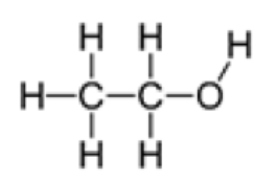
Alkenes and Halogens
- Halogens can be added to alkenes. When halogens react with an alkene, the C=C bond opens. This forms a saturated molecule, where each carbon is bonded to a halogen atom. There is a single bond between the carbon atoms.
- Bromine, chlorine and iodine are examples of halogens. Halogens such as bromine, chlorine and iodine can react with halogens. When iodine reacts with ethene, diiodoethane would be formed, as 2 iodine molecules are involved.
- Reaction conditions: Halogens react with alkenes readily at room temperature and pressure, without the use of a catalyst.
Worked example: Draw the structural diagrams to show the reaction of propene with iodine. Name the product.
Answer: One of the iodine atoms must add to one of the carbon atoms with the double bond, and the other iodine atoms added to the other carbon atom.

The product is di-iodopropane.
Alkenes are a type of organic molecule that contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are characterized by the presence of a carbon atom with two double bonds, which makes them unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Alkenes in GCSE Chemistry are typically liquid or gas at room temperature, with low boiling points and high vapor pressures. They are also highly flammable and can be easily ignited, making them useful as fuels and solvents.
Alkenes in GCSE Chemistry can undergo a variety of chemical reactions, including addition reactions, elimination reactions, and polymerization reactions. Some of the most common reactions of alkenes include addition of hydrogen (hydrogenation), addition of halogens (halogenation), addition of hydrogen halides (hydrohalogenation), and addition of water (hydration).
Hydrogenation in GCSE Chemistry is the addition of hydrogen to alkenes, resulting in the formation of alkanes. This reaction is typically performed using a catalyst, such as nickel or platinum, and is an important industrial process used in the production of margarine, shortening, and other hydrogenated fats.
Halogenation in GCSE Chemistry is the addition of halogens, such as chlorine or bromine, to alkenes. This reaction results in the formation of halogenated alkenes, which are typically more reactive and have different physical and chemical properties compared to the starting alkene.
Hydrohalogenation in GCSE Chemistry is the addition of hydrogen halides, such as hydrogen chloride or hydrogen bromide, to alkenes. This reaction results in the formation of haloalkanes, which are typically more reactive and have different physical and chemical properties compared to the starting alkene.
Hydration in GCSE Chemistry is the addition of water to alkenes, resulting in the formation of alcohols. This reaction is typically performed using a catalyst, such as sulfuric acid or an enzyme, and is an important industrial process used in the production of alcohols for use as fuels, solvents, and chemicals.
It is important to study the reactions of alkenes in GCSE Chemistry because they are a fundamental component of many industrial processes, including the production of fuels, solvents, and chemicals. Understanding the reactions of alkenes is essential for understanding the chemistry behind these processes and for designing new processes and products. Additionally, understanding the reactions of alkenes is essential for understanding a wide range of chemical concepts and processes, including organic synthesis, reaction mechanisms, and product analysis.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment