Silicon Dioxide, Diamond & Graphite (GCSE Chemistry)
Examples of Giant Covalent Structures
Giant covalent structures all consist of covalent bonds and are extremely strong. However, they all have slightly different properties and uses which we will be discussing in this tutorial. Below are a few examples that you are required to know:
Silicon Dioxide (Silica)
- In silicon dioxide, each silicon atom forms four covalent bonds with four oxygen atoms. In silica, each silicon atom shares electrons with four oxygen atoms. This means that each silicon atom forms a single covalent bond with four oxygen atoms.
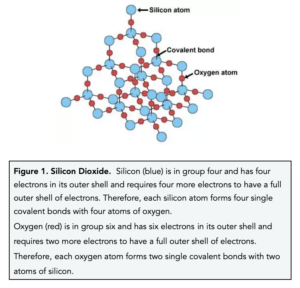
- Silicon Dioxide has a high melting and boiling point. The many covalent bonds in silica are very strong, therefore a large amount of energy is needed to break them therefore a high temperature is required.
- Silica is naturally found as sand. The majority of the sand on beaches is made up of silicon dioxide. Furthermore it is also found in limestone and as quartz in granite.
Diamond
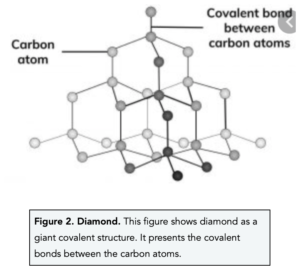
- In diamond, each carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four other carbon atoms. In diamond, each carbon shares electrons with four other carbon atoms. This means that each carbon atom forms a single covalent bond with four other carbon atoms. Each covalent bond is very strong.
- Diamond is a very hard substance due to its strong covalent bonds. The many strong covalent bonds in diamond means that it is very difficult to break. It is actually known to be the hardest naturally occurring substance found on Earth. As a result of its hardness, diamond is often used to coat drill bits and in cutting tools.
- Diamond has a high melting and boiling point. The many covalent bonds in diamond are very strong, therefore a large amount of energy is needed to break them.
- Diamond is a good conductor of heat. Diamond is a good thermal conductor because of the strong covalent bonds it consists of. This means that when you heat the diamond, the vibrations of thermal energy are rapidly transferred through the substance.
- Diamond is a poor conductor of electricity. Diamond cannot conduct electricity because the outer electrons found in each carbon atom are fixated between the atoms in covalent bonds. This means there are no free electrons that can move around and carry charge.
Graphite
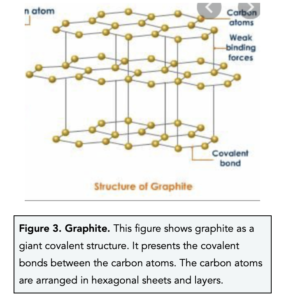
- In graphite, each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds with three other carbon atoms. In graphite, each carbon shares electrons with three other carbon atoms. This means that each carbon atom has one outer electron that is not involved in a covalent bond. This ‘fourth’ electron becomes delocalised and is free to move around.
- The carbon atoms in graphite are organised into sheets of hexagons. In graphite, the carbon atoms are arranged into sheets of macromolecules which means that graphite has a layer structure. The sheets are arranged into layers and the layers are joined together by weak intermolecular forces.
- Graphite is is soft slippery substance because it consists of layers that can slide. Unlike diamond, graphite is arranged in layers and sheets of carbon atoms. The layers in graphite can easily slide over each other because there are weak intermolecular forces holding them together. Due to its slippery nature, graphite can be used in pencils and as a dry lubricant.
- Graphite has a high melting and boiling point. The covalent bonds in graphite are very strong, therefore a large amount of energy is needed to break them.
- Graphite is a good conductor of electricity. Graphite can conduct electricity because it contains delocalised electrons which are free to move between the sheets of carbon atoms and carry charge. Therefore, graphite is used in batteries and as electrodes during electrolysis.
- Graphite has a low density because the distance between the layers is large. As the layers in graphite are held together by weak intermolecular forces, the layers are far apart.
Worked example: Compare and explain the bonding and properties of diamond and graphite ( 6 marks)
Answer
Explain the bonding:-
Diamond and graphite are both made from carbon. (1)
In diamond there are four strong covalent bonds per carbon atom, whereas in graphite there are three strong covalent bonds per carbon atom. (1)
Graphite is organised in layers of macromolecule held together by weak intermolecular forces. (1)
Explain the properties: –
Both diamond and graphite have many strong covalent bonds, so lots of energy is needed to break the bonds and melt both substances. They have very high melting points. (1)
Diamond cannot conduct electricity as there are no delocalised electrons. Graphite can conduct electricity as there are many delocalised electrons which can carry a current throughout the structure. (1)
Diamond is very hard and strong as it is made of many strong covalent bonds. Graphite is soft and slippery as it has weak intermolecular forces between the layers. (1)
Silicon Dioxide is a chemical compound made up of silicon and oxygen. It is a naturally occurring mineral that can be found in various forms such as quartz, sand, and glass.
Diamond is a naturally occurring mineral made up of carbon atoms arranged in a crystal structure. It is the hardest known mineral and is often used for jewelry and industrial applications.
Graphite is a naturally occurring mineral made up of carbon atoms arranged in a layered structure. Unlike diamond, graphite is soft and slippery, making it useful for applications such as pencil lead and lubricants.
Silicon Dioxide and Diamond are both minerals made up of different elements. Silicon Dioxide is made up of silicon and oxygen, while Diamond is made up of carbon. Graphite is also made up of carbon, but its atomic structure is arranged differently than Diamond, giving it different properties.
Silicon Dioxide has a variety of uses, including being a main component of glass, sand, and quartz. It is also used as a food additive, in cosmetics, and as a filler in some rubber and plastic products.
Diamond is often used for jewelry due to its hardness and brilliance. It is also used in various industrial applications such as cutting, drilling, and grinding due to its hardness.
Graphite is often used as a lubricant due to its slippery texture. It is also used as the “lead” in pencils, as a moderator in nuclear reactors, and as an electrode in batteries.
No, Silicon Dioxide is not a good conductor of electricity and is often used as an insulator in electronic devices.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment