Group 7 (GCSE Chemistry)
Group 7
Group 7 – The Halogens
Elements that are non-metals are found on the right hand-side of the periodic table. They are also known as the halogens. Through this tutorial we will be exploring the physical and chemical properties of the halogens and the trends through group 7.
Physical properties of the halogens
- How does the mass and boiling point change down Group 7? As you go down group 7, the relative atomic mass increases and the boiling point of halogens also increases. So fluorine has the lowest atomic mass and the lowest boiling point whereas astatine has the highest atomic mass and the highest boiling point.
- The boiling point is affected by the intermolecular forces. Between atoms of a particular element, there are weak attractive forces known as intermolecular forces. When molecules are boiled or melted, these intermolecular forces are overcome.
- Down group 7, the melting and boiling points increase. The atoms increase in size, as they gain extra electron shells, and the intermolecular forces become stronger. More energy is required to break these forces, thus there are higher melting and boiling points as you go down the group.
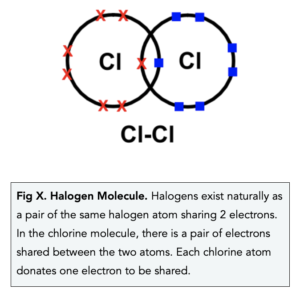
- Halogens have covalent bonding. The halogens are naturally found as simple molecules – a pair of halogen atoms sharing a pair of electrons, this is known as covalent bonding.
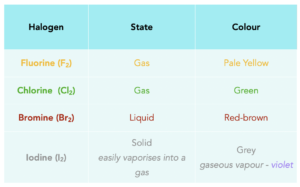
Below is a table that summarises the states of the halogens and their colours.
Chemical properties of the halogens
All atoms of group 7 elements have the same properties and react in the same way, this is because all halogens have 7 electrons in their outermost shell. They need to gain one electron to make a full outermost shell. This can happen in two ways:
- By reacting with a non-metal and forming covalent compounds and
- By reacting with a metal and forming ionic compounds.
Group 7, also known as the halogens, is a group of elements in the periodic table that includes fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. In GCSE Chemistry, students learn about the properties and characteristics of these elements.
The halogens have common properties such as being highly reactive, forming compounds with other elements, and having high electron affinity. In GCSE Chemistry, students learn about these properties and how they relate to the chemical behavior of the halogens.
The electron configuration of the halogens in the outermost energy level is seven electrons. This is why they are referred to as Group 7 elements. In GCSE Chemistry, students learn about the electron configurations of elements and how they relate to their chemical properties.
The halogens react with other elements by forming compounds. They readily gain electrons from other elements to form negative ions. In GCSE Chemistry, students learn about the reaction patterns of the halogens and how they are used in various chemical processes.
The trend in reactivity for the halogens is that the reactivity decreases as you go down the group. Fluorine is the most reactive halogen, while astatine is the least reactive. In GCSE Chemistry, students learn about the trends in reactivity for the halogens and how they can be explained by the properties of the elements.
The halogens have many practical uses such as in the production of disinfectants, bleaches, and refrigerants. They are also used in the manufacture of synthetic dyes, plastics, and pharmaceuticals. In GCSE Chemistry, students learn about the various applications of the halogens and their importance in everyday life.
Studying the halogens is important because they play a significant role in many chemical processes and have numerous practical applications. In GCSE Chemistry, students learn about the properties and behavior of the halogens and how they can be used in various industries. This helps to develop a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles of chemistry and how they can be applied to real-world problems.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment