Ionic Formulae & Diagrams (GCSE Chemistry)
Ionic Formulae & Diagrams
Predicting Reactions of Ions
- Deducing the formula of an ionic compound. When ions react, they react to form neutral ionic compounds. The overall charge of any ionic compound must be zero, so the ionic charges in the compound must balance.
- Working out the formula. The formula of a compound can be calculated by comparing the charges of the ions present in the compound. For example, if there are two ions present in an ionic compound where one has a charge of +1 and the other has a charge of -2. Two positive ions will be needed to balance the charge of the -2 ion.
Working out the Formula
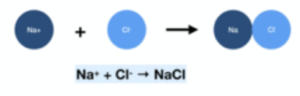
- Group 1 + Group 7. For example, sodium chloride would require one Na+ ion and one Cl– ion to form a neutral compound.
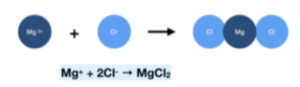
- Group 2 + Group 7. For example, magnesium chloride would require one Mg2+ ion and two Cl– ions to form a neutral compound.
The Swap and Drop Method
- Group 1 + Group 6. For example, potassium oxide would require two K+ ion and one O2– ion to form a neutral compound. (Image like above).
- Group 2 + Group 6. For example, calcium oxide would require one Ca2+ ion and one O2– ion to form a neutral compound. (Image like above)
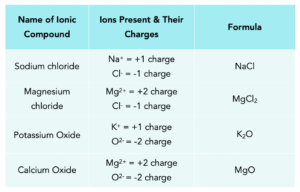
This table below re-iterates the above, by showing how the charges need to balance out mathematically:
Dot and Cross Diagram
In a dot and cross diagram, electrons from one atom are shown as dots and electrons from another atom as crosses.
Worked Example: Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the formation of sodium chloride.
When the two elements react together, the sodium atom loses its outermost electron and the electron is transferred to a chlorine atom.
1.Work out the charges on each ion. Once the chorine atom gains the electron it becomes a chloride ion with a -1 charge.Once the sodium atom loses the electron it becomes a sodium ion with a +1 charge.
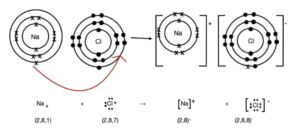
2. Draw the dot and cross diagram. A dot and cross diagram is used to show the transfer of electrons. However, usually only the electrons in the outermost shell are shown.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment