Alkanes (GCSE Chemistry)
Alkanes
Alkanes
General Formula for Alkanes
- The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2. Alkanes are part of a homologous series, which means that they are part of a series of compounds with the same general formula and have similar reactions.
- Using the general formula.The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2. We can use the general formula to work out the number of carbon atoms given the number of hydrogen atoms and vice versa.
Worked example: An alkane has 20 hydrogen atoms. Deduce the number of carbon atoms and formula for the alkane.
1. Use the general formula CnH2n+2 and rearrange for n.
n = [(number of hydrogens) – 2]/ 2
2. Substitute for numbers from the question.
2n+2 = 20, then n = (20-2)/2 = 9
3. Use the number of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms to deduce the molecular formula = C9H20.
More About Alkanes
- Alkanes have single carbon-carbon bonds (C-C). Alkanes are the simplest type of hydrocarbon. All of the carbon-carbon bonds they contain are single covalent bonds, which means that they are saturated compounds (ie no double bonds are present).
- Methane is an example of an alkane. The first member of the alkane family is methane, which has one carbon and four hydrogen atoms. The next three members in order are ethane (2 carbons), propane (3 carbons) and butane (4 carbons).
- Finding the number of carbon atoms. You can deduce the number of carbon atoms in any organic compound using the stem of its name:
meth = 1 carbon atom
eth = 2 carbon atoms
prop = 3 carbon atoms
but = 4 carbon atoms
pent = 5 carbon atoms
Representing Alkanes
For exams, we need to be able to recognise alkanes in various forms.
Sometimes, the compounds will be written in their molecular formula. For example, methane can be written as CH4.
Compounds can also be represented in their displayed structural formula. For example, methane can be written as shown below.
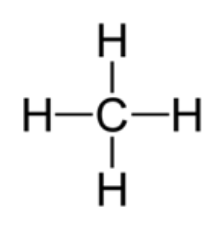
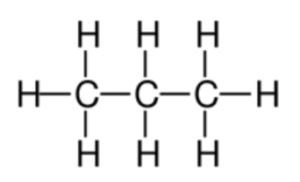
Worked example: Draw the displayed structural formula of propane.
Answer: The formula for propane is C3H8. This is because the stem for the name is “prop” which means there are 3 C atoms. Using the general formula, this means there are 8 H atoms.
Substitution Reactions
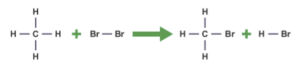
As the name suggests, in a substitution reaction one atom is substituted for another. For GCSE Chemistry, you need to know about the substitution reaction in alkanes with halogens, such as chlorine.
This reaction occurs in the presence of ultraviolet light. Here is an example:
methane + chlorine→ methylchlorine + hydrogen chloride
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment