Ionic Compound Properties (GCSE Chemistry)
Ionic Compound Properties
Properties of ionic compounds
- The physical properties of an ionic compound is determined by its structure. The arrangement of ions in the compound determines whether or not the compound can conduct electricity as well as the melting and boiling point of the compound.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points. The melting and boiling points of ionic compounds is usually quite high because the ions in the giant ionic lattices are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction which are difficult to overcome. A large amount of energy is needed to break these forces (ionic bonds) therefore a high temperature is required.
- Ionic compounds can only conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in solution. Ionic compounds can only conduct electricity when molten or dissolved because only then are the ions of the compound able to move and carry charge. Ionic compounds are unable to conduct electricity when solid because the ions are fixed in place and unable to carry charge.
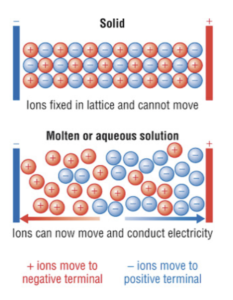

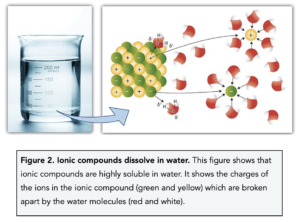
- Ionic compounds are soluble in water. Ionic compounds easily dissolve in water which means they are highly soluble in water. This is because both ionic compounds and water molecules are partially charged molecules (polar). This means the partial charges of water break apart the ionic lattice, pulling oppositely charged ions apart and the ionic compound to dissolve.
Ionic compounds are chemical compounds made up of positively charged ions (called cations) and negatively charged ions (called anions). These ions are held together by electrostatic forces in a repeating crystal lattice structure.
Ionic compounds have several unique properties, including high melting and boiling points, electrical conductivity in a molten or dissolved state, and poor electrical conductivity in the solid state. They are also typically brittle and have a crystal-like structure.
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because the electrostatic forces holding the ions together are strong and require a lot of energy to break. This energy is released as heat when the ionic compound melts or boils.
The crystal structure of ionic compounds affects their properties because it determines the arrangement of ions and the strength of the electrostatic forces holding them together. The repeating crystal lattice structure gives ionic compounds their crystal-like appearance and contributes to their high melting and boiling points.
The electrical conductivity of ionic compounds changes when they are melted or dissolved because the ions become free to move, allowing them to conduct electricity. In the solid state, the ions are held in a fixed position and cannot conduct electricity.
Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in their solid state because the ions are held in a fixed position and cannot move to conduct electricity. However, they may become electrically conductive if they are melted or dissolved in a solvent.
The electrical conductivity of ionic compounds is typically much lower in the solid state compared to that of covalent compounds. Covalent compounds are usually non-conductive in their solid state, but may become conductive if they are melted or dissolved.
No, ionic compounds cannot conduct electricity through their solid lattice structure because the ions are held in a fixed position and cannot move to conduct electricity.
The properties of ionic compounds can be used in a variety of real-world applications, including the production of materials with high melting points, such as ceramics and glass, and in the production of electrolytes for batteries and other electrical applications.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment