Anodes and Cathodes (GCSE Chemistry)
Anodes and Cathodes
The Anode and Cathode
- There are two electrodes. One electrode is positive, whilst the other is negative. Both will direct current through an electrolyte, which the substance being split.
- The anode is positive. The anode is the positive electrode and attracts negative ions. Here, the ions lose electrons, so are oxidised. Metals or hydrogen are usually formed at the anode.
- The cathode is negative. The cathode is the negative electrode and attracts positive ions. Here, the ions gain electrons, so are reduced. Non metals are usually formed at the cathode.
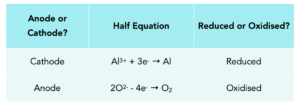
Practice Question 1: Write out the half equations for Aluminium Oxide, stating which is reduced and which is oxidised.
2Al2O3 → 4Al + 3O2
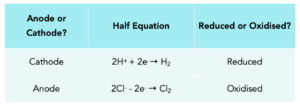
Practice Question 2: Write out the half equations for Sodium Chloride, stating which is reduced and which is oxidised.
2H+ + 2Cl– → H2 + Cl2
When a halide isn’t present in the solution, we have a different half equation at the anode:
4OH– → O2 + 2H2O + 4e–





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment