Group 1: Reactions (GCSE Chemistry)
Group 1: Reactions
Group 1 – reactions with oxygen
All group 1 metals react quickly with oxygen in the air to produce a metal oxide. Below is a generic formula that represents the alkali metals (X) reacting with oxygen to form a metal oxide:
4 X (s) + O2 (g) → 2 X2O (s)
Group 1 elements are stored in oil this is to prevent them from reacting spontaneously with oxygen. When these metals are left out, the oxygen in the air reacts with the surface of the metal forming a white oxide that coats the surface.
They can also be heated in glass jar full of oxygen, where they burn strongly with a flame forming a metal oxide. Some elements form mixtures of a metal oxide (X2O), metal peroxide (X2O2) and metal superoxide (XO2). Below is a table describing the observations made when the first three elements in group 1 react with oxygens and the equations.
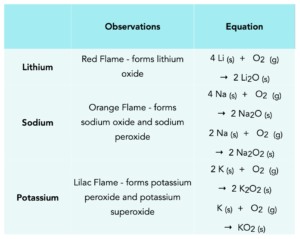
Group 1 – reactions with water
All group 1 metals react vigorously with water to produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen. The Group 1 metals floats on the surfaces and fizzes vigorously. Below is a generic formula that represents the alkali metals (X) reacting with water:
2 X (s) + 2 H2O (l) → 2 XOH (aq) + H2 (g)
These metal hydroxides (XOH) are soluble in water and represented as being aqueous (aq). They form a colourless solution. When a universal indicator is added to measure the pH of the solution it turns purple, this suggests that the solution is highly alkaline. Hence, group 1 elements are also known as alkali metals.
Below is a table describing the observations made when the first three elements in group 1 react with water and the equations.
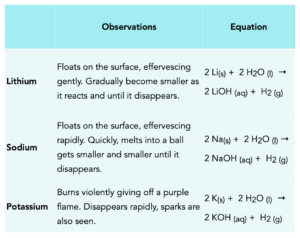
Group 1 – reactions with chlorine
All group 1 metals react vigorously with chlorine gas forming white salts or colourless crystals known as metal chlorides. Below is a generic formula that represents the alkali metals (X) reacting with chlorine:
2 X (s) + Cl2 (g) → 2 XCl (s)
All alkali metals have 1 electron in their outermost shell. During this reaction the alkali metal X loses the electron in its outermost shell and forms a +1 ion. Chlorine then gains that electron, to form a chloride ion (Cl–). The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other and form a metal chloride (XCl).
Chemical reactions are processes that convert one set of chemical substances into another. These reactions involve the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, leading to the creation of new substances.
The signs of a chemical reaction include the production of gas, a change in temperature, the formation of a solid, a change in color, and the release of light or heat.
An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of heat. This type of reaction is characterized by a decrease in the overall energy of the system, and the energy is released to the surroundings.
An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that absorbs energy in the form of heat. This type of reaction is characterized by an increase in the overall energy of the system, and energy must be added to the system from the surroundings in order to proceed.
A balanced chemical equation is a chemical equation that has an equal number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. This means that the same amount of matter is present before and after the reaction.
A reactant is a substance that takes part in a chemical reaction and is present at the start of the reaction. Reactants are transformed into products during the reaction.
A product is a substance that is formed as a result of a chemical reaction. Products are formed from reactants during the reaction.
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed or changed by the reaction. Catalysts work by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, allowing the reaction to proceed more quickly.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment