Separating Mixtures (GCSE Chemistry)
Separating Mixtures
Mixtures and Compounds
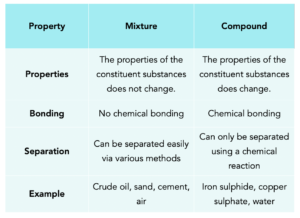
Mixtures
A mixture is made from two or more elements or compounds being mixed together, without the formation of any chemical bonds. This diagram represents the differences between elements, compounds and mixtures.
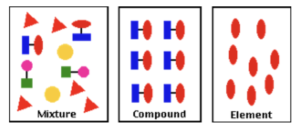
- The chemical property of each substance in a mixture does not change. When elements or compounds are mixed together, the chemical properties of the individual substances do not change. This is because there are no chemical bonds between substances in a mixture.
- Mixtures can be separated by physical processes. Substances in a mixture can be separated using physical processes. These processes do not involve any chemical reactions or the formation of new substances.
- Mixtures come in different states. You can get a mixture of liquids (e.g. oil), a mixture of solids (e.g. different grains in sand), or a mixture (e.g. water and sand in cement).
Compounds
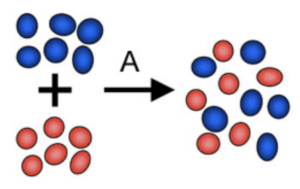
A compound is made from two or more elements which are chemically bonded together.
- Compounds involve chemical bonding. Compounds are different to mixtures because they involve actual chemical bonds between the substances.
- The chemical properties change when compounds are formed. Substances bonded together in a compound, the chemical properties of the compounds do change. For example, iron is magnetic, but when it reacts with sulphur to form iron sulphide, it is no longer magnetic.
Separating Mixtures
In the next few tutorials we will discuss different physical processes that can be used to separate mixtures. First, here are a few key definitions that will help understand the processes better:
- Solvent. The liquid in which a solute dissolves to form a solution
- Solute. The dissolved substance in a solution
- Solution. The mixture formed by a solute and a solvent
Mixtures can be separated using physical processes such as filtration, crystallisation and distillation.
Separating Mixtures in Everyday Life
Waste and Ground Water
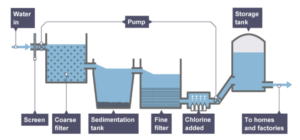
Waste and ground water can be made potable through separation processes including sedimentation, filtration and chlorination.
- Large objects are removed. For example branches and leaves are removed by screens with holes in them.
- Insoluble particles are removed. A coarse filter bed removes these particles.
- Smaller insoluble particles are removed. This is done using a fine bed filter.
- Finally harmful microorganisms are removed. Chlorine gas can be added to remove any harmful substances.
Seawater
Similarly salty sea water can be made drinkable using simple distillation. By boiling the seawater and cooling the water vapour, pure water is formed. This means the water no longer contains salt, so is drinkable. This process can be quite expensive as a lot of energy is required to heat large quantities of water.
Water used in chemical analysis must not contain any dissolved salts which would interfere, so water produced by distillation would be useful in this case.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment