Titration Calculations (GCSE Chemistry)
Titration Calculations
Titration Calculations
Practice Question: Lyra has performed a titration with 25.0cm3 of 0.300mol/dm3 sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH) which is neutralised by 0.100mol/dm3 sulfuric acid (H2SO4). What is the volume of the H2SO4 used?
1.Write out the balanced equation. Similar to the moles questions, we need to write out the balanced equation and then draw our table.
2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
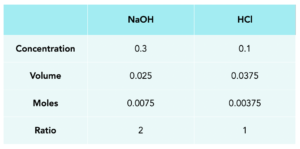
2. Fill in the known values. In this question, we know the NaOH volume and concentration. We also know the H2SO4. We need to remember to cover the units of volume from cm3 to dm3.
cm3 to dm3 = divide by 1000
3. Work out the number of moles of each substance. Using the information that we’ve got, we can work out the number of moles.
moles = concentration x volume
4. Use the ratio. From the balanced equation, we can see that the ratio of the reactants is 2:1.
Moles of H2SO4 = 0.00375
5. Calculate volume of H2SO4.
volume = moles/concentration.
6. Convert into the correct units. We need to give our answer in cm3.
dm3 to cm3 = multiply by 1000
Answer is 0.0375dm3 or 37.5cm3.
Practice Question 2: James has performed a titration with 25.0 cm3 of 0.100 mol/dm3 of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution which was neutralised by exactly 20.0 cm3 of a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid (HCl). What is the concentration of the HCl?
Similar to the first question, we need to figure out the balanced equation and use a table to calculate the concentration.
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
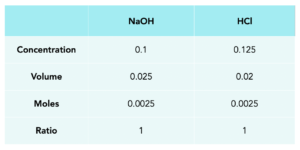
1.Fill in the known values. These are the NaOH volume and concentration, plus the HCl volume. Remember to convert the units of volume from cm3 to dm3 dividing by 1000.
2. Work out the number of moles.
moles = concentration x volume
3. Work out the ratio. We can use the balanced equation to do this.
Ratio = 1:1
Moles for HCl will be 0.0025.
4. Calculate the concentration. Now that we have moles and volume, we can calculate concentration.
concentration = moles/volume.
Answer = 0.125mol/dm3
FAQs
Titration is a method used to determine the unknown concentration of a solution by reacting it with a known concentration of another solution.
The steps involved in a titration are: preparing the solution to be titrated, preparing the solution with known concentration (titrant), adding the titrant to the solution being titrated, and determining the end point of the reaction.
Titration is used in GCSE chemistry to accurately determine the concentration of an unknown solution. It is a common laboratory technique that helps students understand chemical reactions and stoichiometry.
The calculation for titration depends on the specific type of titration being performed. In general, the calculation involves using the known concentration and volume of one solution and the volume of the other solution to determine the concentration of the unknown solution.
Here are the general steps for calculating titration:
Determine the balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place during the titration.
Measure a known volume of the solution of known concentration using a volumetric flask or pipette.
Add a small amount of an indicator to the solution to signal the endpoint of the titration.
Slowly add the solution of unknown concentration to the solution of known concentration while stirring, until the endpoint is reached (the indicator changes color).
Record the volume of the solution of unknown concentration that was added to reach the endpoint.
Use the balanced chemical equation to determine the moles of the reactants in the reaction.
Use the known concentration and volume of the solution of known concentration and the volume of the solution of unknown concentration to calculate the concentration of the unknown solution.
The formula for molarity in titration is: Molarity = moles of solute/volume of solution (in liters).
The endpoint in a titration is the point at which the reaction between the two solutions is complete. It is determined by observing a change in color or by using a pH meter.
Some common indicators used in titration include phenolphthalein, bromothymol blue, and methyl orange.
To improve the accuracy of a titration, you should carefully measure the volume of both the solution being titrated and the titrant, use a calibrated burette, and use a suitable indicator to determine the endpoint.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment