The Xylem (A-level Biology)
The Xylem
Plants need a transport system to make sure all of its cells get a sufficient amount of nutrients. This can be achieved through the combination of xylem and phloem tissue.
Xylem tissue enables water, as well as dissolved minerals, to travel up the plant in the passive process of transpiration.
Vascular Bundle in The Plant
In the Roots
- Xylem and phloem are found within vascular bundles in the stem. Vascular bundles are strands of vascular tissue containing xylem and phloem vessels that distribute water and organic substances around the plant and serve as structural support.
- X-shape arrangement in the centre of the vascular bundle. This is to make sure the plant can withstand the various mechanical forces, for example, pulling.
- Surround by endodermis. By surrounding the X-shape arrangement with endodermis, an outer layer of cells, the xylem vessels are supplied with water.
- Inner layer of cells. The inner layer of the xylem vessels are meristem cells, also known as the pericycle.
In the Stem
The placement of the xylem inside non-wooded plants provide support and flexibility.
With the phloem lying outside the vascular bundle, a layer of cambium is found between the two tissues. It is meristem cells which aid in the production of new xylem and phloem tissue.
In the Leaf
The vascular bundles form the midrib and veins.
Monocotyledonous (cereals) and dicotyledonous crop plants (broad-leaved crops, such as carrots and potatoes) leaves help in the processes of transport and support of xylem and phloem tissue. This is because they have a network of veins which start at the midrib and outwards.
Xylem Vessels
Xylem tissue transports water and minerals in the stem and leaves of plants. Water and minerals are first absorbed by the plant roots, and the xylem vessels then transport them to the rest of the plant.
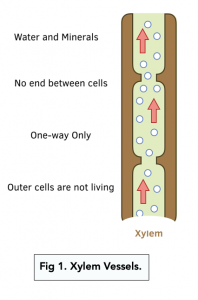
Xylem vessels are long, hollow tubes made up of dead cells. The cells that make up the vessels have no end walls, so a continuous tube forms that water can move through, going upwards only.
Xylem vessels contain pits. These allow water to move sideways between the vessels. Lignin is a tough substance which thickens the vessels, though it is deposited in a spiral-shape to allow them to remain flexible.
Xylem is a type of plant tissue responsible for transporting water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. It is an essential component of the plant’s vascular system and plays a crucial role in maintaining the plant’s overall health and growth.
Xylem is important in Biology because it helps to provide essential nutrients and water to the plant, which is vital for its growth and survival. It also plays a role in the plant’s ability to withstand stress and disease, making it an important topic for understanding the overall biology of plants.
Xylem works by using transpiration pull and root pressure to move water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. The water and nutrients are absorbed by the roots and then move up through the xylem vessels, where they are distributed to the rest of the plant.
Transpiration pull is the process by which water is drawn up the xylem vessels due to the loss of water through the stomata on the leaves. As water evaporates from the leaves, it creates a negative pressure that pulls water up from the roots, keeping the plant hydrated.
Root pressure is the pressure that is exerted by the roots of the plant to move water and nutrients up the xylem vessels. This pressure is created by the active transport of ions and other solutes into the root cells, which then exerts pressure on the surrounding water.
The main components of Xylem are the xylem vessels, tracheids, and parenchyma cells. The xylem vessels and tracheids are responsible for transporting water and nutrients, while the parenchyma cells play a supporting role in the xylem tissue.
Xylem and Phloem are two different types of plant tissue, each with its own specific functions. Xylem is responsible for transporting water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant, while Phloem is responsible for transporting sugars and other organic compounds from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
Xylem plays a role in plant adaptation by allowing plants to transport water and nutrients over long distances, enabling them to grow in a variety of different environments. Additionally, the structure and composition of xylem can change in response to environmental conditions, allowing plants to adapt to changes in water availability and other environmental factors.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment