Factors Affecting Cell Membrane Structure (A-level Biology)
What is a Cell Membrane Structure in A-Level Biology?
In A-Level Biology, the cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer that surrounds the cell and separates its internal environment from the external environment. It is also known as the plasma membrane.
The structure of the cell membrane is described as a fluid mosaic model, which means that it is made up of a mosaic of different components that are able to move around and change position within the membrane. The main components of the cell membrane include:
- Phospholipid bilayer: This is the main component of the cell membrane and consists of two layers of phospholipid molecules. Each phospholipid molecule has a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-fearing) tail. The hydrophilic heads face outward towards the aqueous environments, while the hydrophobic tails face inward and form a barrier that prevents water-soluble substances from passing through the membrane.
- Proteins: These are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer and have a variety of functions, such as acting as channels or pumps to allow specific molecules to pass through the membrane, or as receptors to allow the cell to respond to signals from other cells or the environment.
- Carbohydrates: These are attached to the surface of the membrane and help to identify the cell and its function. They are involved in processes such as cell recognition and cell-to-cell communication.
- Cholesterol: This is found within the phospholipid bilayer and helps to maintain the fluidity of the membrane. It helps to prevent the membrane from becoming too rigid or too fluid, allowing it to function optimally.
Overall, the structure of the cell membrane is crucial to the functioning of the cell, as it allows the cell to maintain a stable internal environment while also interacting with the external environment.
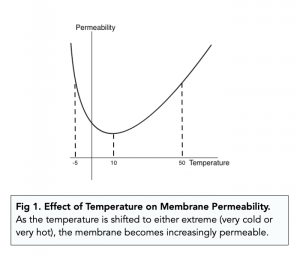
Effect of Temperature on (A-Level Biology) Cell Membrane Structure
This is one of the common factors affecting (A-Level Biology) Cell Membrane Structure
- Cell membranes are sensitive to temperature. Changes in temperature can affect the fluidity and permeability of cell membranes, which impacts cell structure and function.
Below 0°C
- Increase in membrane rigidity. As the temperature drops to below zero, phospholipids lose much of their kinetic energy. Therefore, the membrane loses its fluidity which causes it to become very rigid.
- Increase in membrane permeability. Proteins within the membrane become heavily denatured, which increases the permeability of the membrane. Ice crystals can form in the membrane, which can cause the membrane to fracture, especially during thawing, which also increases permeability.
0°C – 45°C
- Membranes are fluid. Between 0-45°C, phospholipids can easily move (although their movement is naturally restricted by cholesterol).
- Membranes are semi-permeable. At these temperatures, the membrane is also semipermeable. As temperatures increases, the kinetic energy of the phospholipids also increases, which increases their movement. This increase in movement leads to an increase in permeability of the membrane.
Above 45°C
- Phospholipid bilayer begins to break down. Increasing kinetic energy allows the phospholipids to move far away from each other, which destroys the structural integrity of the membrane, causing it to “melt”.
- Cell Membrane Structure becomes freely-permeable. Transport and channel proteins denature, thus making them unable to regulate what gets into and out of cells, which leads to increased membrane permeability.
- The membrane may burst. The heat causes water inside of the cells to expand which puts pressure on the membrane, causing it to burst.
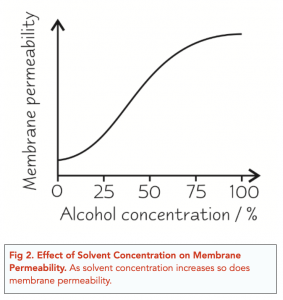
Effect of Solvents on Cell Membrane Structure
- Solvents such as ethanol increase membrane permeability. Lipids dissolve in alcohol, therefore, the phospholipids in a cell membrane will easily dissolve in solutions such as ethanol. As a result, the cell membrane becomes more fluid and permeable as it starts to break down.
- The effect on membrane permeability depends on solvent type. Certain types of solvent can cause a greater degree of membrane permeability than others, for example, ethanol causes greater membrane permeability than methanol.
- Increasing solvent concentration increases membrane permeability. Solvent concentration and membrane permeability are directly correlated i.e. increasing solvent concentration increases membrane permeability. This is because as the solvent becomes more and more concentrated, it has a greater ability to dissolve phospholipids and disrupt the membrane structure, making it more permeable to external substances.
Practical Investigations into Cell Membrane Permeability
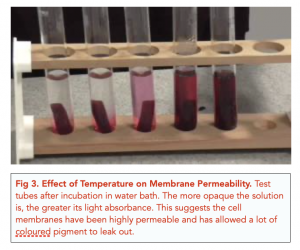
We can design an investigation to see exactly how factors such as temperature, solvent type, and solvent concentration affect membrane permeability. This experiment is typically done with beetroot, a highly pigmented vegetable. As the cell membranes become disrupted and more permeable, the coloured pigment leaks out, which can be measured to quantify the degree of cell membrane permeability.
Investigating the effect of temperature on Cell Membrane Structure
- Cut beetroot into five equal sized pieces. Wash these pieces afterwards to remove any pigment that leaked out while cutting.
- Pipette 5 cm3 of water into five different test tubes.
- Prepare water baths at five different temperatures. E.g. 20°C, 30°C, 40°C, 50°C, and 60°C.
- Place each test tube in the different water baths. They all need to be incubated for the same duration.
- Remove the test tubes from the water baths. Carefully remove the beetroot pieces, leaving the remaining coloured liquid in the test tubes.
- Using a colorimeter (as discussed in tutorial 17), measure how much light is being absorbed by the liquid in each test tube.
- The greater the absorbance, the more coloured, or opaque, the liquid in the test tube is. This means that there has been a greater degree of permeability within the beetroot’s cell membranes, resulting in a large amount of pigment leaking out.
Investigating the effect of solvent concentration on Cell Membrane Structure
- Cut and wash five equal sized pieces of beetroot.
- Prepare 5 different test tubes with 5cm3 of the following concentration of solvents:
- Water
- 10% Ethanol
- 30% Ethanol
- 50% Ethanol
- 70% Ethanol
- Put each piece of beetroot into the different test tubes. Seal the test tube openings with a rubber bung and shake the tubes.
- Leave the beetroot pieces submerged for an hour. Periodically shake the tubes during this duration.
- After an hour, carefully remove the beetroot pieces from the solution. Use a glass rod to help you fish out the pieces. Leave the remaining coloured liquid behind.
- Use a colorimeter to measure light absorbance by the liquid in each test tube.
FAQs
The cell membrane structure can be affected by factors such as temperature, pH, cholesterol levels, and the presence of certain proteins and lipids.
An increase in temperature can cause the cell membrane to become more fluid and lead to a change in its shape and structure. On the other hand, a decrease in temperature can cause the membrane to become more rigid and disrupt normal cell function.
The cell membrane is sensitive to changes in pH and a shift in pH can alter the charge distribution and fluidity of the membrane, potentially leading to changes in its structure and function.
Cholesterol is an important component of the cell membrane and helps to regulate its fluidity. High levels of cholesterol in the membrane can lead to a decrease in fluidity and stability, while low levels of cholesterol can cause the membrane to become more fluid and lead to disruptions in cell function.
Proteins and lipids play a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of the cell membrane. The presence of specific proteins and lipids can affect the fluidity and stability of the membrane, and changes in their levels can result in changes in the membrane’s structure and function.
Yes, changes in cell membrane structure can significantly affect cell function. The cell membrane is responsible for controlling the movement of molecules and ions into and out of the cell, and changes in its structure can disrupt these processes and result in changes in cell function.
The permeability of cell membranes can be affected by several factors, including:
Temperature: Higher temperatures can increase the fluidity of the membrane and cause the phospholipids to move around more, which can increase its permeability.
Solvents: Certain solvents, such as alcohols or detergents, can dissolve the lipid bilayer and disrupt the structure of the membrane, leading to increased permeability.
pH: Extreme pH levels can affect the charges on the membrane proteins and lipids, which can alter the structure of the membrane and affect its permeability.
Presence of certain molecules: Some molecules, such as hormones, can bind to receptors on the membrane and cause changes in the structure of the membrane, which can affect its permeability.
Lipid composition: The lipid composition of the membrane can affect its permeability. For example, the presence of unsaturated fatty acids can increase the fluidity of the membrane, while the presence of cholesterol can decrease it.
Presence of transport proteins: Transport proteins in the membrane can affect the permeability of the membrane by facilitating the movement of specific molecules across the membrane.
Overall, the permeability of the cell membrane is a highly regulated process that can be affected by a variety of factors. The proper functioning of the cell membrane is crucial for the survival of the cell and its ability to maintain a stable internal environment.
Temperature can affect the structure of a cell membrane by altering its fluidity. At lower temperatures, the phospholipid molecules in the membrane are packed closely together and are less mobile, making the membrane more rigid and less permeable. This can restrict the movement of molecules across the membrane, which can affect the proper functioning of the cell.
At higher temperatures, the phospholipid molecules in the membrane move around more and are more fluid, making the membrane more permeable. This can allow molecules to move across the membrane more easily, but can also lead to damage or destruction of the membrane if the temperature becomes too high.
Furthermore, high temperatures can also cause the denaturation of membrane proteins, such as transport proteins and receptors, which can affect their ability to function properly. This can lead to an imbalance of ions and other molecules across the membrane, which can affect the overall functioning of the cell.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment