Protein Formation (A-level Biology)
Protein Formation
Peptide Bonding
Proteins are formed when amino acids become linked to each other via peptide bonds.
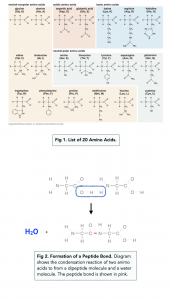
- Condensation reactions join amino acids. Condensation reactions lead to formation of strong covalent bonds, called peptide bonds, which hold the amino acids together. Water is also released during the reaction.
- Condensation reactions can form dipeptides or polypeptides.
-
- Two amino acids linked to each other are known as a dipeptide.
- Several amino acids linked together are known as a polypeptide.
-
- Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides.
- Peptide bonds can be broken down by hydrolysis reactions. This can break proteins and peptides down to their constituent amino acids.
- There are 20 common amino acids present in living organisms. The only difference between them is the R side group.
- Glycine is the smallest amino acid. In glycine the R group is just a hydrogen atom.
There is no need to memorise the amino acids below, but use Figure 1 to understand the ways in which amino acids can differ.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment