How Muscles Allow Movement (A-level Biology)
How Muscles Allow Movement
Skeletal Muscle Effectors
Key Terms
Skeletal muscle is muscle connected to the skeleton, which is used to create movement.
Tendons are collagen fibres which connect skeletal muscles to bones.
Ligaments connect bones to other bones.
Antagonistic Pairs
- Skeletal muscles transfer force to bones to allow for movement. The bones are incompressible which allows the muscles to pull against them, and are connected by collagen fibres called tendons.
- A single muscle can either contract or flex. A muscle can contract and pull on a bone to flex a joint, but it cannot push the bone back to its original position. To allow joints to both extend and bend, separate muscles are needed.
- Muscles work in antagonistic pairs. These muscles in combination are known as antagonistic pairs – the coordination of an agonist muscle (contracting) and an antagonist muscle (relaxing). One muscle in the pair will contract whilst the other is relaxed.
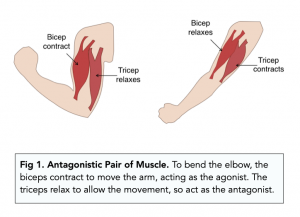
Example: Elbow Joint
- To bend the elbow, the biceps contract to move the arm, acting as the agonist. The triceps relax to allow the movement, so act as the antagonist.
- To extend the elbow, the triceps contract to extend the arm, acting as the agonist. The triceps relax to allow the movement, so act as the antagonist.
Muscles are specialized tissues in the body that are capable of contracting and relaxing to produce movement. In A-level Biology, students learn about the different types of muscles, including skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
In A-level Biology, students learn that muscles allow movement by contracting and relaxing in response to signals from the nervous system. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and work in pairs to produce movement. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the bone to which it is attached, causing movement. For example, when the bicep muscle contracts, it pulls on the forearm bone, causing the arm to bend.
In A-level Biology, students learn about the process of muscle contraction, which involves the sliding of thin filaments made of protein called actin past thick filaments made of protein called myosin. This sliding produces movement and generates force, allowing the muscle to contract. The process of muscle contraction is controlled by the release of a chemical called acetylcholine from nerve impulses, which triggers the sliding of the actin and myosin filaments.
Understanding how muscles allow movement is an important concept in A-level Biology as it provides insight into the functioning of the human body and the mechanisms of movement. By studying this topic, students gain a deeper understanding of the anatomy and physiology of muscles, including their structure and function, and learn how they interact with other systems in the body to produce movement. This knowledge is critical for understanding a wide range of biological processes, including human movement and athletic performance, and is useful in fields such as sports science, medicine, and rehabilitation.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment