DNA Structure and The Double Helix (A-level Biology)
DNA Structure and The Double Helix
Structure of DNA
- A single strand of DNA has two different ends. Due to the orientation of the deoxyribose sugar, there are two ends:
-
-
- The starting point of a single DNA strand is known as the 5’ (five prime) end.
- The end point of a single DNA strand is known as the 3’ (three prime) end.
-
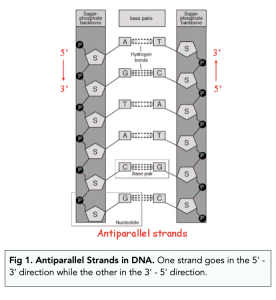
-
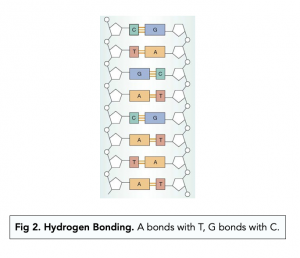
- Adenine forms a complementary base pair with thymine through two hydrogen bonds..
-
- Guanine forms a complementary base pair with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds.
- There are no other base pairing combinations in DNA. The above rules are the only pairings that exist. Exceptions to this rule are mutations, which are abnormal and can have serious consequences for an organism.
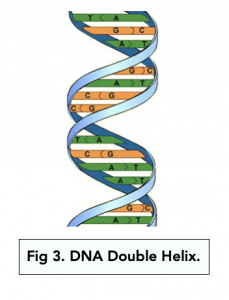
- A DNA double helix is formed. The two antiparallel polynucleotide chains twist to form a helical shape called the “DNA Double Helix”.
Purifying DNA
We can extract and purify the nucleic acids from the DNA of different biological samples through a precipitation reaction. The process involves breaking down the cells in the sample and causing the DNA to precipitate so that it can be separated from the rest of the solution.
- Detergent and salt are added to the sample solution containing the biological sample. The detergent breaks down the lipid membranes in the sample while the salt neutralises the charge in the DNA’s phosphate backbone.
- The solution is heated to further break down the DNA. The high heat denatures enzymes in the cells as well as breaking down the DNA further.
- Protease enzymes breaks down proteins bound to the DNA. The solution needs to first be cooled in an ice bath and filtered. Then protease enzymes, which breaks down peptide bonds, can be added to the solution so that any proteins bound to the DNA can be separated.
- Ethanol helps the DNA to precipitate. DNA is not soluble in alcohol. As such, adding ethanol to the solution allows the DNA to precipitate on top of the solution and be separated from the rest of the cellular material. You can then take out this precipitate with a glass rod.
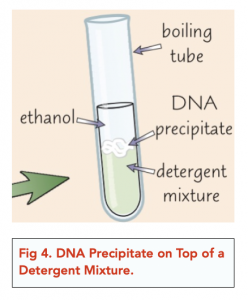
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the development and functioning of all living organisms.
The double helix structure of DNA refers to its spiral shape, where two complementary strands of nucleotides run in opposite directions and are held together by hydrogen bonds.
Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA, composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. They make up the two complementary strands of the DNA molecule and hold the genetic information.
The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases pair up in specific ways (A with T and C with G) to form the rungs of the DNA ladder.
The base pairing in DNA is significant because it allows the DNA molecule to store and transmit genetic information. The specific pairing of the nitrogenous bases ensures that the genetic information is accurately copied during cell division.
DNA replication occurs when the two complementary strands of the DNA molecule separate and each strand acts as a template for the formation of a new complementary strand. This results in the creation of two identical DNA molecules.
DNA plays a crucial role in genetic inheritance as it contains the instructions for the development and functioning of an organism. During cell division, the genetic information contained in the DNA is passed on to the daughter cells, ensuring that the characteristics of the parent cell are preserved.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment