Hyperpolarisation and Transmission of the Action Potential (A-level Biology)
Hyperpolarisation and Transmission of the Action Potential
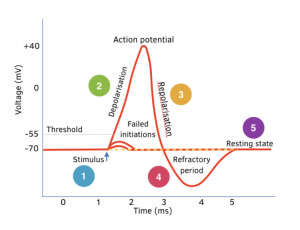
Transmitting an Action Potential
Hyperpolarisation and Resting Potential
4. Hyperpolarisation – Potassium channels close more slowly, which means many Kᐩ ions can diffuse out of the axon, so the membrane becomes hyperpolarised (-90mV).
5. Resting Potential – Resting potential is re-established by the sodium-potassium pump. This is called the refractory period, during which no other action potential can be generated.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment