The Phloem (A-level Biology)
The Phloem
Plants need a transport system to make sure all of its cells get a sufficient amount of nutrients. This can be achieved through the combination of xylem and phloem tissue.
Phloem tissue enables sugars to reach every part of the plant in the active process of translocation.
Phloem
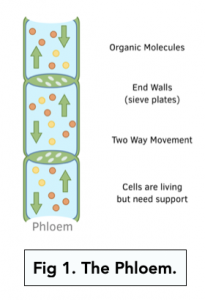
- Phloem tissue transports organic substances in plants. These organic substances include sugars, such as sucrose, and some mineral ions, which travel as the dissolved form of sap. They go to storage organs and growing areas of the plant. The process is known as translocation. Transport is multidirectional.
- Phloem tissue consists of living sieve tube elements that each have a companion cell. Sieve tube elements do not have organelles because they form the tube that transports the organic substances. Instead, the companion cells contain the organelles to carry out metabolic reactions.
- Companion cells help with ATP (energy) production. This is to aid in active processes.
- Links through plasmodesmata. The cytoplasm in the sieve tube elements and companion cells are linked by gaps (known as plasmodesmata) between cells walls. This allows communication and flow of substances.
The Phloem in A-Level Biology is a type of tissue in plants that is responsible for transporting food and nutrients from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
The function of the Phloem in A-Level Biology is to transport food and nutrients from the leaves to other parts of the plant. This is done through a process known as translocation.
The Phloem in A-Level Biology transports food through a process known as translocation. This involves the movement of sugars and other nutrients from the source, such as the leaves, to the sink, such as the roots or developing fruits and seeds.
The components of the Phloem in A-Level Biology include the sieve elements, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma. The sieve elements are the main conducting cells, while the companion cells are responsible for metabolic support and regulation. The phloem parenchyma are storage cells that store food and nutrients.
Translocation in the Phloem in A-Level Biology is the process of moving food and nutrients from the source, such as the leaves, to the sink, such as the roots or developing fruits and seeds. This process involves the movement of sugars and other nutrients through the Phloem tissue.
The Phloem in A-Level Biology is important because it plays a crucial role in the transport of food and nutrients throughout the plant. This allows the plant to grow and develop properly, and also helps it to survive in challenging environments.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment