Proteins and Amino Acids: An Introduction (A-level Biology)
Proteins and Amino Acids: An Introduction
Proteins are biological molecules that are made up of small monomers i.e. amino acids.
Structure of Amino Acids
- Amino acids are the monomers of proteins.
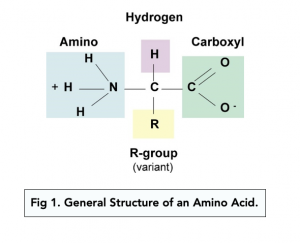
- There are 20 amino acids and they all have very similar structures. On one end, they contain an amine group (-NH2). This is known as the N-terminus. On the opposite end they contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) which makes them an acid. This is known as the C-terminus.
- The amine group and carboxyl group are covalently bonded to a central carbon atom. The central carbon atom is bonded to one hydrogen (H) atom, and a variable “R” group.
- The variable “R” group is different for each amino acid. This variable group is what gives each amino acid its unique chemical and physical properties. This group is also commonly known as the side chain.
- Different amino acids can be grouped together based on their “R” groups.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment