Biodiversity Calculations (A-level Biology)
Biodiversity Calculations
Calculating Biodiversity
Simpson’s Diversity Index (D)
Simpson’s Diversity Index (D) is a measure of the relationship between the number of different species in a habitat (species richness) and the number of individuals within each species (species evenness).
Simpson’s Diversity Index can be calculated using the following formula:
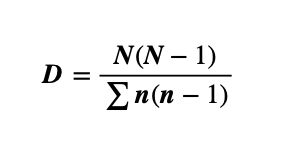
D = Simpson’s Diversity Index
Σ = sum of
N = total number of organisms of all species
N = total number of organisms of each species
A highly biodiverse and stable environment will have a high D value. This also indicates that the particular environment has “good biological health”.
In contrast, an unstable and non-biodiverse environment will have a low D value. This also indicates that the particular environment has “poor biological health”.
Practice Question
Work out the Simpson’s Diversity Index for Population A and B.
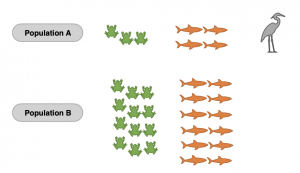
Population A
There are 8 organisms in total, so N(N-1) is 8(7) = 56
There are 3 toads, so n(n-1) for toads is 3 (2) = 6
There are 4 fish, so n(n-1) for fish is 4 (3) = 12
There is 1 heron, so n(n-1) for herons is 1 (0) = 0.
D = 56 / (6 + 12) = 3.11
Population B
There are 24 organisms in total, so N(N-1) is 24(23) = 552
There are 12 toads, so n(n-1) for toads is 12 (11) = 132
There are 12 fish, so n(n-1) for fish is 12 (11) = 132
D = 552 / (132 + 132) = 2.09
Biodiversity refers to the variety of different species and ecosystems that exist within an area. It includes the variety of different plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, as well as the diversity of habitats and ecosystems that they live in. Biodiversity is an important aspect of the natural world and is crucial for maintaining a healthy and functioning ecosystem.
Biodiversity is important because it helps to maintain a healthy and stable ecosystem. Each species within an ecosystem plays a specific role, and the loss of even one species can have a significant impact on the entire ecosystem. Biodiversity is also important for human well-being, as it provides us with resources like food, medicine, and fuel, and helps to regulate the Earth’s climate and protect against natural disasters.
There are several methods for measuring biodiversity, including species richness, species evenness, and functional diversity. Species richness measures the number of different species within an area, while species evenness measures the distribution of those species. Functional diversity measures the different roles and functions that species play within an ecosystem.
The species richness formula is simply the total number of species within a particular area. It is often represented by the symbol “S” and is calculated by counting the number of different species present within a defined area.
The species evenness formula is used to measure the distribution of species within an area. It takes into account not only the number of species, but also their relative abundance. The most commonly used formula for species evenness is the Pielou’s Evenness Index, which is calculated by dividing the natural logarithm of the number of species by the natural logarithm of the total number of individuals in the sample.
The functional diversity formula measures the different roles and functions that species play within an ecosystem. There are several different metrics that can be used to calculate functional diversity, including the functional richness and functional divergence formulas. These formulas take into account the specific traits and abilities of different species and how they contribute to the functioning of the ecosystem.
Biodiversity calculations can help in conservation efforts by providing important information about the variety of species and ecosystems within a particular area. This information can be used to identify areas of high biodiversity that are in need of protection, and to monitor changes in biodiversity over time. By understanding the diversity and distribution of species, conservation efforts can be targeted and prioritized to protect the most important and vulnerable areas.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment