Weight and Mass (GCSE Physics)
Weight and Mass
Weight and Mass
Differences between Weight and Mass
- There is a difference between mass and weight. Weight is determined by the action of gravity, whereas mass is not. This means that wherever you are in the Solar System, your mass will be the same, but your weight will not. Therefore mass resists changes in motion.
- Weight is a force. Weight is measured in newton’s and changes according to the force of gravity. This means that your weight on the Earth is different to your weight on the Moon.
- Mass is just a value. Mass is the ‘amount’ of object that you have. Your mass on Earth would be the same as your mass on the Moon.
Weight and Mass are Directly Proportional
- Weight and mass are directly proportional. Weight and mass are closely linked, and are said to be directly proportional. This means that they do the ‘same thing’. If the mass halves, then the weight will half. If the mass triples, then the weight will triple.
Measuring Weight
Centre of Mass
- The centre of mass will be at the centre of a symmetrical object. The centre of mass is the point at which the object will balance. It is often found in the centre of a symmetrical object.
Using a Newtonmeter
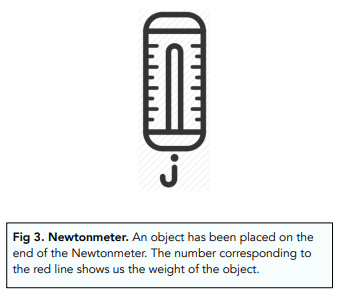
- Newtonmeters are used to measure weight. Newtonmeters are calibrated spring-balances, which are used to measure weight. When an object is placed onto the end of the newtonmeter, the spring will extend. Then the force (weight) can be read off the scale.
Stability
The stability of an object can be affected by the:
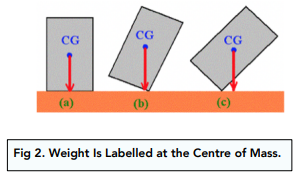
- Position of the centre of gravity. The lower the centre of gravity, the more stable the object. The higher the centre of gravity, the less stable the object. It is more likely to topple over.
- Area of the base. An object with a larger overall base area will be more stable. For example, think about a tall glass compared to a mug. The mug has a larger base surface area and is much less likely to topple over than the glass.
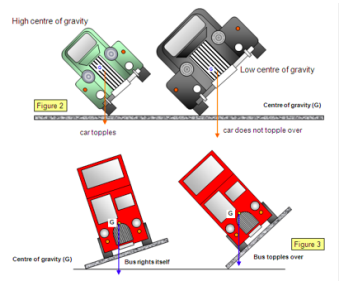
Combining these two factors determines the stability of an object. If the objects centre of gravity does not pass through the base when it is tilted, it will topple over
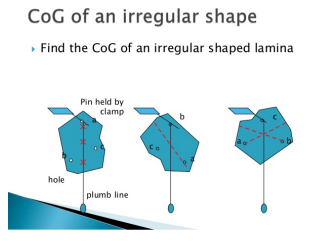
Finding the Centre of Mass of an Irregular Shaped Object
Method
- Gather your equipment. You will need a clamp, a plumb line, a pin and a lamina.
- Attach the object. Attach the irregular shaped lamina to a pin.
- Allow the card to swing. Hang up the card and let it turn until the centre of mass is vertically under the pin.
- Attach a plumb line. Repeat using a plumb line. Mark the position of the thread.
- Repeat. Mark the position of the thread at least two more times, changing the position of the pin.
- Determine the centre of mass. The point at which the lines cross is the centre of mass.
Weight is a measure of the force of gravity acting on an object. It is calculated as the mass of an object multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity.
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and does not have direction.
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is a measure of the force of gravity acting on an object. Weight depends on the local gravitational field, while mass is a constant property of an object, regardless of its location.
Weight is measured using a scale, which measures the force exerted by an object on the scale. This is then converted to a weight measurement in units such as grams or pounds.
Mass is measured using a balance, which compares the mass of an object to a known mass. This is typically done using a laboratory balance, which measures mass to a high degree of precision.
Weightlessness is the state in which an object experiences no force of gravity acting on it. This can occur in a state of free fall or in orbit around the Earth, where the acceleration due to gravity is effectively zero.
An object has weight on Earth because it is being acted upon by the force of gravity. In space, away from any significant gravitational fields, an object experiences no force of gravity and is said to be weightless.
Weight changes with altitude because the acceleration due to gravity decreases with increasing altitude. At higher altitudes, the force of gravity acting on an object is weaker, resulting in a lower weight measurement.
Yes, an object can have a mass but no weight. This can occur in a state of weightlessness, such as in orbit around the Earth or in a state of free fall.
The weight of an object changes on different planets because the strength of the local gravitational field is different on each planet. The weight of an object on a given planet is determined by its mass and the local acceleration due to gravity on that planet.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment