Magnification (GCSE Physics)
Magnification
Magnification
Magnification is a ratio and so has no units.
Calculating Magnification
We can calculate magnification using the following formula:

Where:
- Image height in cm or mm (if the object height is in mm, then the image height must be in mm).
- Object height in cm or mm (if the image height is in cm, then the object height should be in cm).
Magnification has no units since it is a ratio.
Question: An object that is 5cm tall produced an image 250cm tall. What is the magnification?
1. Write out the equation.
In this instance, our equation will be magnification = image height / object height.
2. Substitute in the numbers.
magnification = image height / object height
magnification = 250 / 5
magnification = 50
Converging Lenses
Magnifying Glasses
A single convex lens can be used to make an object to appear larger than it really is, or in other words magnify an object.
The object must be placed less than one focal length’s distance away from the lens. Therefore, we can say that the image is upright, enlarged and virtual.
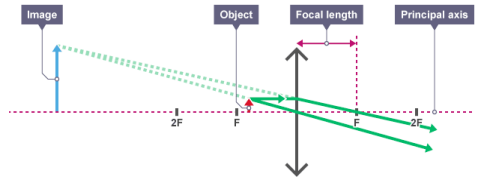
Real Images
If the object is placed between one and two focal lengths away from the lens, the image will be real, enlarged and inverted.

If the object is placed more than twice the focal length away from the lens, the image will be real, diminished and inverted.
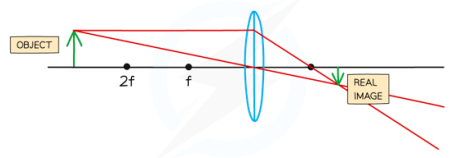
If the object is placed exactly twice the focal length from the lens, the image will be real, the same size as the object and and inverted.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment