Thermistors and LDRs (GCSE Physics)
Thermistors and LDRs
Thermistors
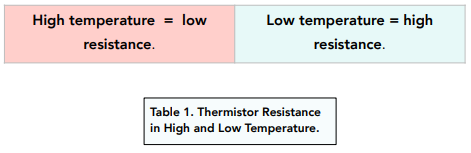
A thermistor is a special type of resistor. This resistor depends on the temperature of the surroundings. The higher the temperature, the lower the resistance.
Applications in Circuits
There are several applications of thermistors:
- Digital Thermostat – when a thermistor is placed inside a thermostat, it can sense the temperature of the surroundings. In this way, it forms part of the circuit and enables efficient temperature control of our homes. For example, if it gets too hot, the thermistor will have lower resistance, allowing more current to flow to potentially cool the room.
- Replacement Fuse – a fuse is used to break a circuit when it becomes dangerous, thus preventing an accident. Instead of using a fuse, we can use a thermistor. If too much electricity flows in a circuit, the circuit and thermistor will heat up. This increases the resistance of the thermistor, which increases the flow of current and therefore prevents the circuit from becoming dangerous.
Light Dependent Resistors
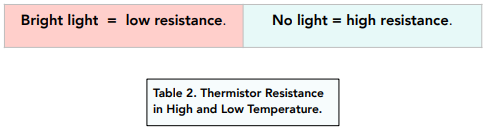
Light dependent resistors are often called LDRs. Similar to how a thermistor depends on temperature, an LDR will depend on light.
Applications in Circuits
There are several applications of LDRs:
- Burglar Detectors – LDRs can be used in burglar detectors. When light falls on the sensor, the resistance will decrease. This allows a signal or security alert to be triggered. In this way, LDRs can be used as part of a security system.
- Street Lights – LDRs can be used in automatic street lights. They work by using the light in the surroundings, and therefore can switch the streetlights on and off appropriately
FAQs
A thermistor is a type of resistor that changes its resistance based on the temperature. They are used in a variety of applications, such as temperature control and sensing.
The two types of thermistors are negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistors and positive temperature coefficient (PTC) thermistors. NTC thermistors have a lower resistance when the temperature increases, while PTC thermistors have a higher resistance when the temperature increases.
An LDR, or Light Dependent Resistor, is a resistor that changes its resistance based on the amount of light it is exposed to. They are commonly used in light sensors, such as automatic lighting systems and cameras.
An LDR works by changing its resistance based on the amount of light it is exposed to. When there is more light, the resistance of the LDR decreases, and when there is less light, the resistance increases.
Some applications of thermistors and LDRs include temperature control and sensing, automatic lighting systems, cameras, and various other electronic devices that need to respond to changes in temperature or light.
Thermistors and LDRs differ from each other in the type of change they respond to. Thermistors respond to changes in temperature, while LDRs respond to changes in light.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment