Energy Transfers in Electronic Appliances (GCSE Physics)
Energy Transfers in Electronic Devices
Power
The power of an appliance is the amount of energy (J) that it transfers per second.
In other words, power is the rate of energy transfer.
Energy is transferred in everyday appliances, including electronic appliances. For example kettles, microwaves and hairdryers can all convert electrical energy into other forms of energy, which we can then use.
In these electronic devices, energy is transferred from the batteries or ac mains to motors or heating appliances. We will cover this in more detail in the Electricity chapter.
Energy Transfer in Electronic Devices
Work Done and Energy Transfer
Work is done when charge flows in a circuit.
As with any form of ‘work’, energy is transferred when electrical work is done.
We can calculate energy transferred by electrical work in two ways, by using:
- Power and time.
- Charge and voltage.
In this tutorial we will look at energy transferred in a circuit, using power and time. We will cover energy transferred using charge and voltage in the Electricity section of the course later on.
Using Power and Time
Here’s a reminder of the power equation we learnt in tutorial 12. Power tells us the energy transferred per second. To find the total energy transferred over a sustained period of time, we need to multiply power by the total number of seconds.
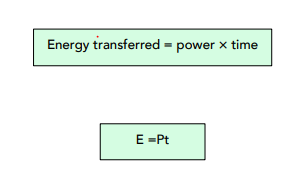
Where:
- energy transferred, E, in joules, J
- power, P, in watts, W
- time, t, in seconds, s
Question: An electric lamp transforms 350J in 10s. What is its power?
- Write out the equation.
In this instance, we need to rearrange the equation to make power the subject.
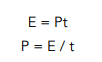
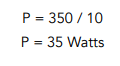
Question: A motor has a power of 15W. How much energy does the motor transfer in 2 minutes?
E = P t = 15 x 120 = 1800J
Question: Rita is deciding between purchasing a lamp from Aryaland and a lamp from Makam Bulbs. The lamp from Aryaland has a power of 5W, whilst the lamp from Makam Bulbs has a power of 8W.
Assuming 100% efficiency in both lamps, what is the difference in the kilojoules (kJ) of energy produced in 3 hours?
The difference between the powers: 8W – 5W = 3W
We need the answer in seconds, hence 3 hours = 180 minutes x 60 seconds = 10800 seconds
E = P x T = 3 x 10800 = 32400
To convert to kilojoules: 32400/1000 = 32.4kJ
Power Ratings and Energy
- The power rating is a maximum value. When a customer buys an electrical device, it comes with a power rating. This is the maximum value at which the appliance can be used safely. We also know that power is the rate of energy transfer. Therefore, the power rating also tells us the maximum rate at which energy can be transferred when using the appliance.
- Power ratings can vary. Some power ratings are low, whilst others are high. We know that electrical device can store energy. A high power device will be transfer more of this energy per second, therefore doing more work. By doing so, a high power device will require more electricity.
Energy transfer in electronic appliances refers to the movement of energy from one form to another within the appliance. This allows the appliance to perform its intended function, such as heating, cooling, or providing light.
The different forms of energy include electrical, thermal, kinetic, and potential energy.
Energy transfer in electronic appliances takes place through a combination of electrical and thermal energy transfer. Electrical energy is converted into thermal energy, which is used to heat or cool the appliance, or into kinetic energy, which powers the movement of the appliance.
Electrical energy is a type of energy that results from the movement of charged particles, such as electrons.
Thermal energy is a type of energy that results from the movement of particles within a substance, such as a gas or a liquid.
Kinetic energy is a type of energy that results from the movement of an object.
Potential energy is a type of energy that is stored in an object due to its position or state.
Energy transfer in a toaster occurs when electrical energy is converted into thermal energy, which is used to heat the toaster’s heating elements. This thermal energy is then transferred to the bread, causing it to become toasted.
Energy transfer in a refrigerator occurs when thermal energy is transferred from the interior of the refrigerator to the exterior. This is achieved through the use of a refrigeration cycle, which involves the transfer of heat from a coolant, such as refrigerant gas, to the exterior of the appliance.
Understanding energy transfer in electronic appliances is important because it helps to explain how the appliance works and how it can be improved. By improving energy efficiency, electronic appliances can consume less energy and be more environmentally friendly.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment