The Elastic Potential Energy Equation (GCSE Physics)
The Elastic Potential Energy Equation
Calculating EPE
We can use the following formula to calculate the elastic potential energy of an object.
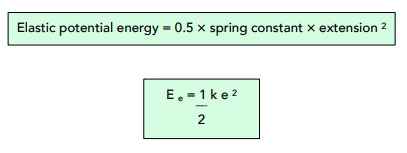
Where:
- elastic potential energy, Ee, in joules, J
- spring constant, k, in newtons per metre, N/m
- extension, e, in metres, m
Question: Callum stretches a spring (which has spring constant 75 N/m). He manages to stretch it from 40cm to 65cm. Calculate the elastic potential energy that is now stored in the spring in Joules.
- Write out the formula.
We need to write out the formula to calculate elastic potential energy.
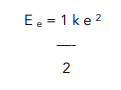
- Calculate the extension.
Before we can calculate anything, we need to find the extension of the spring. In this question, we need to watch out for our units, since the extension should be measured in meters.40cm = 0.4m
60cm = 0.6m
0.6 – 0.4 = 0.2m - Substitute in the numbers.
Now that we have a value for the extension, we can simply put the numbers into our equation. We also need to remember to give the units along with our final answer.
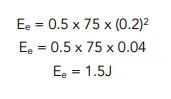
Question: Find the spring constant of a spring that has been extended 28cm and holds 14.6J of energy in its elastic potential store. Give your answer to 2 dp.
- Write out the formula.
We need to write out the formula to calculate elastic potential energy.
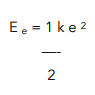
We need to calculate k, the spring constant. Therefore rearrange the equation so k is the subject.
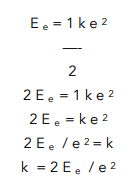
Now that we have k as the subject, we can simply put the numbers into our equation. We also need to remember to give the units along with our final answer.
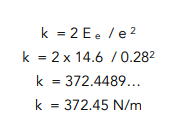
Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in an object as a result of its deformation, or stretching or compression. This energy is stored in the object when it is stretched or compressed, and it is released when the object returns to its original shape.
The elastic potential energy equation in GCSE Physics is given by the formula: U = 1/2 × k × x^2, where U is the elastic potential energy, k is the spring constant, and x is the displacement of the object from its rest position.
The spring constant in the elastic potential energy equation represents the stiffness of a spring, and it determines how easily the spring can be stretched or compressed. The higher the spring constant, the more difficult it is to stretch or compress the spring, and the greater the amount of elastic potential energy that is stored in the spring.
The displacement of an object from its rest position affects the elastic potential energy stored in it. The greater the displacement, the greater the amount of elastic potential energy that is stored in the object. The elastic potential energy stored in an object is proportional to the square of the displacement, as indicated by the x^2 term in the elastic potential energy equation.
Elastic potential energy is related to other key concepts in GCSE Physics, such as work, energy, and forces. Understanding the relationship between these concepts is essential for understanding how elastic potential energy is stored and transferred in physical systems.
Elastic potential energy is used in a wide range of real-world applications, including mechanical springs, elastic bands, and trampolines. Understanding the principles of elastic potential energy is essential for designing and building these and other devices that rely on the storage and transfer of elastic potential energy.
It is important to study the elastic potential energy equation in GCSE Physics because it provides a mathematical way to understand and describe the behavior of physical systems that store and transfer elastic potential energy. Understanding the elastic potential energy equation is also essential for solving problems and making predictions about physical systems in a range of real-world applications.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment