Changes of State (GCSE Physics)
Changes of State
Conserving Mass
- Physical changes are reversible, chemical changes are irreversible. We will come across two types of changes in substances; physical changes and chemical changes. Physical changes can be reversed, but chemical changes cannot be reversed.
- Changes of state are physical changes. When substances change from one state to another, they are undergoing physical changes. The particles making up the substance are the same, but the arrangement and energy of the particles is different.
- During changes of state, mass is conserved. When states change, the amount (and therefore number) of particles stays the same, meaning that mass is conserved. Only the energy and arrangement of the particles will be altered.
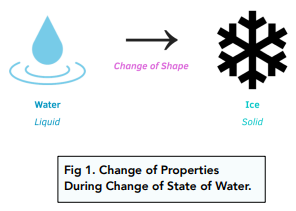
- During changes of state, properties will change. When a substance changes state, it will also change its properties. For example, when water goes from a liquid to a solid (ice), the ice will not be able to take on the shape of the container. However, when ice turns back into water, it will get its original properties back (and the water can take on the shape of the container again).
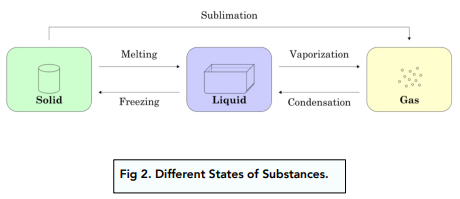
Below is a diagram of the state changes between solids, liquids and gases. For exams, you will need to know the names of the changes between each state, including melting, freezing, evaporation, condensation and sublimation.
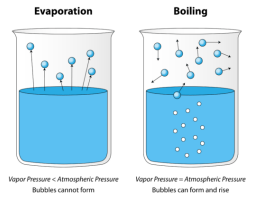
Comparing Evaporation and Boiling
Evaporating and boiling both lead to a change from liquid to gas.
Evaporation
- Evaporation can happen at room temperature. Evaporation can happen at any temperature. For example, if you left a water beaker in room temperature overnight, the volume would drop as some water evaporates.
- Evaporation occurs from the surface of a liquid. If molecules near the surface have enough energy to escape, evaporation will take place. Therefore energy is lost from the liquid and the temperature of the liquid will decrease. This is why evaporation causes cooling.
Boiling
- Boiling can only happen at the boiling point. Boiling can only happen at the boiling point. The boiling point can vary for each substance – e.g. water has a boiling point of 100 degrees celsius, whereas ethanol has a boiling point of 78 degrees celsius.
- Boiling is faster than evaporation. Boiling involves a heat source and often bubbles are seen. The rate of conversion of liquid to gas is much faster than in evaporation. Evaporation can often happen without us noticing.
- Boiling occurs throughout the liquid. Boiling requires an energy input, where all the molecules throughout the liquid gain kinetic energy and move faster, expanding the liquid
Evaporation
Factors Affecting the Rate of Evaporation
- Temperature. The higher the temperature, the more kinetic energy molecules will have to escape as a gas.
- Surface area. The larger the surface area, the more space molecules have to escape.
- Movement of air. If there is an increased movement of air, for example a draft, molecules with less energy can be moved off the surface of the liquid. This will increase the rate of evaporation.
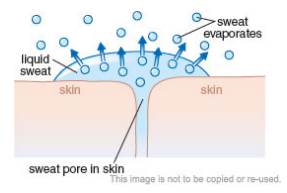
Cooling by Evaporation
An object can be cooled if it comes into contact with an evaporating liquid.
For example our sweat evaporates at room temperature, changing from liquid on the surface of our skin to water vapour in the air. This will cool down the person’s body
Melting and Boiling
You need to be able to define the melting and boiling points, as well as being able to explain condensation and solidification.
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid will melt when heated.
The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid will become a gas when heated.
Condensation occurs when gas molecules in the air lose their kinetic energy as they collide with a cool surface. The gas molecules become closer together and form bonds, becoming a liquid.
Solidification occurs when molecules in a liquid lose their kinetic energy. The molecules become closer together and form tight bonds, forming a solid. This is the same as freezing.
A change of state is a physical change that occurs when a substance transitions from one state of matter to another, such as from a solid to a liquid, a liquid to a gas, or a gas to a solid.
The process that occurs when a solid turns into a liquid is called melting.
The process that occurs when a liquid turns into a gas is called evaporation or vaporization.
The process that occurs when a gas turns into a liquid is called condensation.
The process that occurs when a liquid turns into a solid is called freezing.
The process that occurs when a solid turns directly into a gas is called sublimation.
The process that occurs when a gas turns directly into a solid is called deposition.
During a change of state, the energy of a substance is either absorbed or released as heat. For example, during melting, energy is absorbed as heat and during condensation, energy is released as heat.
The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid is called the melting point.
The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas is called the boiling point.
The melting point and boiling point of a substance are related to each other. The boiling point is usually higher than the melting point for most substances.
A physical change is a change in the physical properties of a substance, such as its state of matter, shape or size, without any change in its chemical composition. A chemical change, on the other hand, involves a transformation of the chemical composition of the substance.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment