Energy Transfers (GCSE Physics)
Energy Transfers
Energy Transfers
- Work done needs a source of energy. Work done involves transferring energy, so we need the energy to come from somewhere before we transfer it. For example, if a person pushes a wheelbarrow, chemical energy is converted to kinetic energy to move the wheelbarrow. The chemical energy originates from the food the person eats.
- The energy transferred includes some wasted energy. Not all of the energy transferred during work is converted into useful energy. For example, if a person pushes a wheelbarrow, most of the chemical energy is converted to kinetic energy to move the wheelbarrow. But some will be converted to heart and sound energy.
Frictional Forces and Temperature Rise
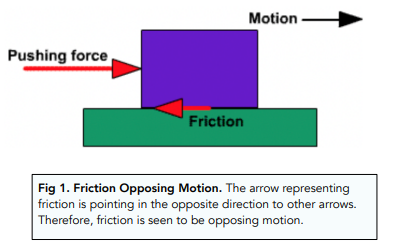
- A frictional force opposes motion. When a moving object experiences friction, its motion will be opposed. As a result, it is harder to move an object over a frictional surface, since more work has to be done (Fig 1).
- Frictional forces result in more work done. When friction is involved, more work has to be done to cover the same distance, because energy is needed to overcome the frictional force. Friction makes it harder to push or pull an object.
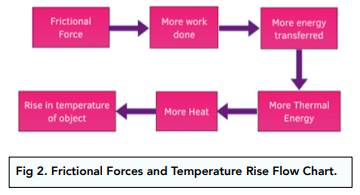
- Friction results in thermal energy. The presence of frictional forces means that some of the energy input is transferred into thermal energy. Seeing as more work is done due to frictional forces anyway, there is a greater amount of energy transfer. This will result in a greater amount of thermal energy.
- Thermal energy leads to a rise in temperature. Thermal energy is another phrase for ‘heat energy’, so it will lead to the production of heat. The heat that is produced will lead to a rise in the temperature of the object.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment