Non-renewable Energy Sources (GCSE Physics)
Non-renewable Energy Sources
Non-renewable Energy Resources
Non-renewable energy resources include fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas) and nuclear fuel (uranium and plutonium).
Characteristics of Non-Renewable Energy Resources
- Non-renewable resources may run out. Fossil fuels are natural resources formed from the living remains of organisms millions of years ago. However, fossil fuels are in limited supply so they will eventually run out.
- Non-renewable resources are reliable. They are readily available and easy to obtain unlike renewable resources such as solar energy, which is dependent on the weather.
- Non-renewable resources are relatively cheap. Fossil fuel power plants are quite cheap to build and manage. The cost to extract fossil fuels is also relatively low.
Environmental Impact
There are several issues caused by non-renewable resources:
- Greenhouse gases – as previously discussed, burning fossil fuels cause to the environment through the production of greenhouse gases. When burnt, non renewable resources release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This CO2 contributes to global warming.
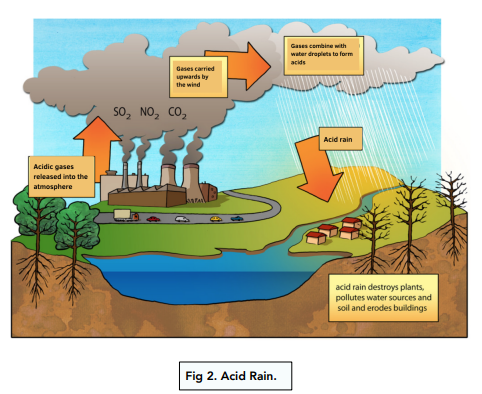
- Acid rain – also through the burning of fossil fuels, we can produce sulphur dioxide, which causes acid rain. The SO2 gas is released into the atmosphere, mixes with rain and produces acid rain. This acid rain
can damage buildings, kill fish in lakes and also be harmful to trees.
Although we know about these environmental effects of using certain energy resources, we cannot always combat these issues. This is because of the following considerations:
- Political – sometimes governments try to introduce charges and taxes to discourage people from doing certain things. For example there is a Congestion Charge in London, where drivers have to pay a fee to be able to drive in a particular area of the capital at certain times. By doing this, the government hoped to decrease the pollution in the capital from fossil fuels.
- Social – although solar panels and wind turbines are good non renewable energy resources, some people don’t want panels on their roof, or a turbine plant in their back garden. These are forms of ‘visual pollution’, which spoil an otherwise aesthetically pleasing view.
- Ethical – when we use nuclear fuels, we produce lots of radioactive waste. This waste is extremely harmful and stays dangerous for hundreds of years. It can be argued that it is unethical to create this type of waste, since it has a tremendous impact on future generations.
- Economical – many renewable energy sources involve a large amount of money to set up. For example, building solar panels, wind turbines and cars that run on biofuels are all incredibly expensive to make. We
have to consider whether all these start up costs will be beneficial in the long run.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment