Ratio of Potential Differences (GCSE Physics)
Ratio of Potential Differences
Ratio of Potential Differences
Number of Turns Ratio
- In a transformer, we know that there is a primary and a secondary coil. The two coils do not have the same potential difference; this varies across the two.
- The pd of each coil is determined by the number of turns on each coil. The higher the number of turns on the coil, the higher the pd in that coil. We can work out a ratio of turns between the primary and secondary coils, and therefore a ratio of p.d.’s as well.
The transformer equation:
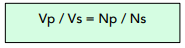
Where:
- The number of turns on the primary coil, Np
- The number of turns on the secondary coil, Ns
- The potential difference of the primary coil, Vp
- The potential difference of the secondary coil, Vs
Question: A transformer has 400 turns on its primary coil and 20 on its secondary coil. Calculate the potential difference across the primary coil if the potential difference across the secondary coil is 12 V.
1. Write out the formula.
Vp / Vs = Np / Ns
2. Write out the numbers we know
Vs = 12V
Np = 400 Turns
Ns = 20 Turns
3. Substitute in the numbers.
Vp / Vs = Np / Ns
Vp / 12 = 400/20
Vp / 12 = 20
Vp = 20 x 12
Vp = 240V





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment