Elastic Potential Energy (GCSE Physics)
Elastic Potential Energy
What is Elastic Potential Energy, EPE?
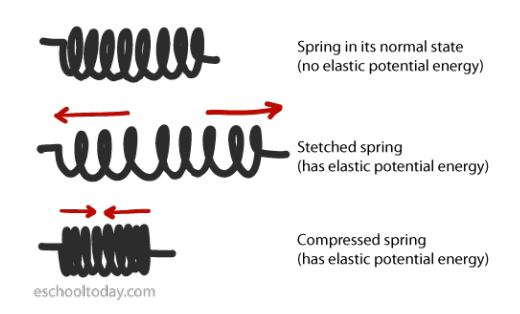
When an object is stretched or compressed, it will gain elastic potential energy. Therefore elastic potential energy is zero in objects which have not been stretched or compressed.
Examples of Elastic Potential Energy
- Springs
When we stretch or compress a spring, we transfer kinetic energy into elastic potential energy.
When you squeeze a stress ball, energy is stored as elastic potential energy. When you release the ball and it returns to its original shape, the stored elastic potential energy will be released.
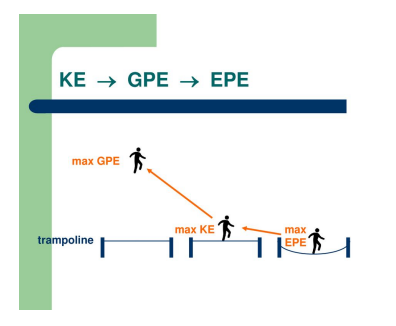
Just before a person jumps onto a trampoline, they carry gravitational potential energy. As they move down towards the trampoline, gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. When the person lands on the trampoline, the springs in the trampoline will stretch. This causes energy to be stored as elastic potential energy in the springs and surface of the trampoline. As the person jumps again, the elastic potential energy is released back into the person.
Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in an object as a result of its deformation. It is the energy that is stored in an object when it is stretched or compressed. This energy is stored due to the elastic force acting on the object, which is proportional to the amount of deformation.
Elastic potential energy can be calculated using the formula: U = 0.5 × k × x^2, where U is the elastic potential energy, k is the spring constant, and x is the amount of deformation of the object. The spring constant is a measure of the stiffness of the object, and the greater the value of k, the greater the elastic potential energy stored in the object.
The spring constant (k) is a measure of the stiffness of a spring or an elastic object. It represents the force required to compress or stretch the object by a certain amount. The spring constant is a constant that depends on the material and shape of the spring and is used to calculate the elastic potential energy stored in the object.
Elastic energy is used in many practical applications, including in springs and elastic bands. For example, springs are used to store energy and release it when needed, such as in a mousetrap or a car suspension system. Elastic bands are used to store energy and release it, such as in a slingshot or a rubber band gun.
Work is defined as the transfer of energy from one system to another. When an object is stretched or compressed, the work done on the object is equal to the change in its elastic potential energy. This means that the amount of work done on an object is directly proportional to the change in its elastic potential energy.
Elastic potential energy is a form of stored energy and is related to other forms of energy such as kinetic energy and thermal energy. For example, when a spring is compressed, the elastic potential energy stored in the spring is converted into kinetic energy as the spring is released and moves. This kinetic energy can then be transferred to other objects and cause thermal energy to be generated as a result of friction and collisions.
When a spring is stretched or compressed, the amount of elastic potential energy stored in the spring changes. If the spring is stretched, its elastic potential energy increases, and if it is compressed, its elastic potential energy decreases. This change in elastic potential energy is a result of the work done on the spring as it is stretched or compressed.
Elastic potential energy is related to Hooke’s law, which states that the force exerted by a spring is proportional to the amount of compression or stretching it experiences. This means that the greater the compression or stretching of a spring, the greater the force it exerts, and the greater the amount of elastic potential energy stored in the spring.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment