Uses of Nuclear Radiation (GCSE Physics)
Uses of Nuclear Radiation
Medical Uses
- Gamma rays are used to treat cancer. Patients with cancer are often treated with a form of gamma rays, called radiotherapy. A strong beam of gamma rays is aimed at the cancerous tissue. The cancerous tissue is killed due to the radiation exposure.
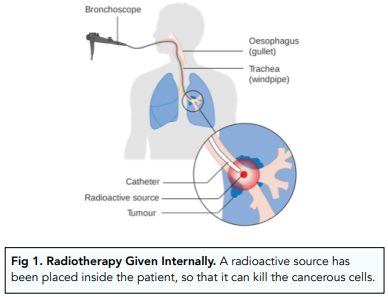
Other uses
- Household fire alarms. During a fire, the smoke absorbs alpha radiation. This then ionises the air inside a smoke detector, triggering the fire alarm to go on.
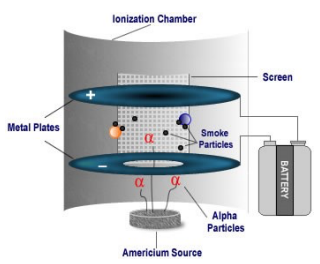
FAQs
Nuclear radiation is a type of radiation that is produced by the nucleus of an atom. It differs from other forms of radiation, such as light and heat, in that it is more energetic and has the ability to penetrate materials. Nuclear radiation can also be harmful to living organisms and the environment.
Nuclear radiation is used in many different applications in everyday life, including medical imaging, cancer treatment, food preservation, and smoke detectors. In medical imaging, nuclear radiation is used to produce images of the inside of the body, such as x-rays or CT scans. In cancer treatment, nuclear radiation is used to kill cancer cells. Nuclear radiation is also used to preserve food by killing bacteria and other microorganisms, and to detect smoke in smoke detectors.
Nuclear radiation is used in medical applications to produce images of the inside of the body, to treat cancer, and to sterilize medical equipment. For example, x-rays, CT scans, and PET scans all use nuclear radiation to produce images of the inside of the body. In cancer treatment, nuclear radiation is used to kill cancer cells and to shrink tumors. Nuclear radiation is also used to sterilize medical equipment to prevent the spread of infection.
The use of nuclear radiation in medicine is just one of many medical technologies available. It is a valuable tool for medical imaging and cancer treatment, but it is not the only option. Other technologies, such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scans, also play an important role in medical diagnosis and treatment. The choice of which technology to use depends on the specific needs of the patient and the medical situation.
One potential risk of using nuclear radiation in medicine is exposure to harmful levels of radiation. This can cause long-term health effects, such as an increased risk of cancer and other diseases. On the other hand, nuclear radiation can also provide many benefits in medicine, such as improved accuracy in medical imaging and cancer treatment, and improved patient outcomes.
Nuclear radiation is also used in other industries, such as food and energy production. In the food industry, nuclear radiation is used to preserve food by killing bacteria and other microorganisms. In energy production, nuclear radiation is used in nuclear power plants to produce electricity.
The study of the uses of nuclear radiation in physics is important because it helps us understand the properties and behavior of nuclear radiation and how it can be used in different applications. This knowledge is essential for advancing our understanding of the fundamental principles of physics and for developing new technologies and applications in the future.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment