Forces in Equilibrium (GCSE Physics)
Forces in Equilibrium
Special Case: Equilibrium Situations
When we use the term equilibrium, we mean that all the forces in the situation are balanced. The resultant force will be equal to zero.
In exams, we can be given specific questions relating to forces in equilibrium. To see if an object is in equilibrium, we can use vectors:
- Draw all the forces. Drawing out the forces should be your first step in this question. Label them all clearly onto a diagram.
- Use a ruler to measure the forces. Measure the lengths of the vectors using a ruler. This will make sure that you are drawing the forces to scale.
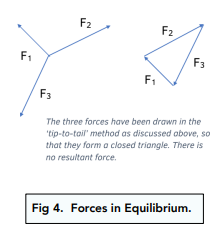
- Rearrange the forces to make a shape. Once you have labelled the forces on a diagram, you can rearrange them to make a shape. If there are 3 forces, it will form a triangle. As you can see in the diagram below, the beginning of one arrow will be touching the end of another arrow.
- Check that there is no resultant force. When forces are in equilibrium, there will not be any resultant force. To check that this, make sure that all the arrows join together to form a closed shape (in Fig 13, the arrows form a closed triangle).





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment