Acceleration (GCSE Physics)
Acceleration
Calculating Acceleration
Formula for Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change in speed of an object. We can calculate acceleration using the following formula:
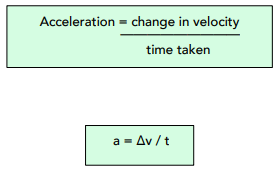
Where:
- acceleration, a, in metres per second squared, m/s²
- change in velocity, ∆v, in metres per second, m/s
- time, t, in seconds, s
Question: A high-speed train accelerates at a constant rate in a straight line. The velocity of the train increases from 30 m/s to 42 m/s in 60 seconds.
1. Calculate the acceleration of the train.
Write out the formula for acceleration.
Acceleration = change in velocity / time taken
2. Work out the change in velocity.
Change in velocity = 42 – 30
Change in velocity = 12 m/s
3. Substitute in the numbers.
Acceleration = change in velocity / time taken
Acceleration = 12 / 60
Acceleration = 0.2 m/s²
Acceleration and Deceleration
- Acceleration means speeding up. When we say that an object is accelerating, we mean that it is speeding up. The speed is increasing and hence the velocity is changing. For example, cars accelerate when you press down on the gas pedal.
- Deceleration means slowing down. When we say that an object is decelerating, we mean that it is slowing down. This means that its speed is decreasing. Compared to acceleration, deceleration is its opposite. Sometimes, we refer to deceleration as ‘negative acceleration’.
Everyday Accelerations
- You need to know everyday speeds. Previously, we have discussed some average speeds for modes of transport including cars, trains and cycling. Using these speeds will help you to estimate the acceleration.
- You need to estimates times. When estimating acceleration, you need to know the time taken by the object as well. Since this is an estimated acceleration, you need to also estimate the time taken.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment