Distance-Time Graph Calculations (GCSE Physics)
Distance-Time Graph Calculations
Calculating Speed from a Distance-Time Graph
Equation to Calculate Speed
The equation for speed is:

The equation for gradient of a distance-time graph is:
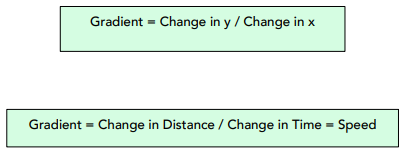
Therefore, by finding the gradient of a distance-time graph, we can find the speed of the object. We will explore this in the following example.
Example
Question: Below is a distance-time graph for part of a train journey. The train is travelling at a constant speed.
Calculate the speed of the train, with units.
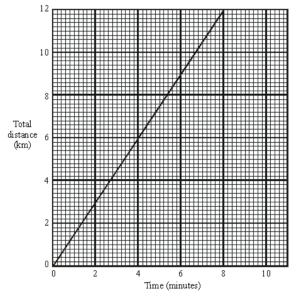
Speed is the gradient. Since this is a distance-time graph, the gradient will tell us the speed of the train.
1. Use the formula for gradient.
To find the gradient of a graph, we use the formula change in y / change in x.
gradient = change in y / change in x = distance / time
2. Find the distance and time.
Using the graph, find values for distance and time.
Distance = 12km
Time = 8 mins
3. Use the equation.
Now that we have values for distance and time, we can use our formula from step 2.
Distance / time = 12 / 8
12 / 8 = 3 / 2
Speed = 1.5 km/min





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment