Using the Gravitational Potential Energy Equation (GCSE Physics)
Using the Gravitational Potential Energy Equation
Calculating the GPE
Sometimes you may be given the gravitational potential energy. So instead you might be asked to calculate the height or the mass of an object.
This can be done by rearranging the gravitational potential energy equation. The following example shows how to calculate the height.
Question: A pear has a GPE of 14J and a mass of 275g. Calculate it’s height in m giving your answer to 2 decimal places. Take the value of g as 9.8 N/kg
- Write out the formula.
Firstly, we need to write out the correct formula for gravitational potential energy.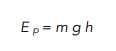
- Rearrange the GPE equation for h.
Move m and g to the other side, so we can solve for h.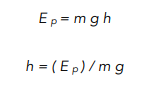
- Substitute in the numbers.
Remember the question asks for h in metres and to one decimal place.
h = 14 / 0.275 x 9.8
h = 14 / 2.695
h = 5.19m (2 d.p)
This process can similarly be repeated to calculate the mass of an object.
Question: An apple has a GPE of 15J and is held at a height of h=225cm above the ground. Calculate the mass of the apple in g. Take the value of g as 9.8 N/kg.
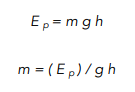
m = ( 15 ) / 9.8 x 2.25
m = ( 15 ) / 22.05
m = 0.68kg
m = 680g
Question: A bee of mass 0.05g lands on a flower. The bee then jumps up above the flower, gaining 1.8 x 10-4 J. How high did the bee rise in cm? Give your answer to 2 d.p. Take the value of g as 9.8 N/kg.
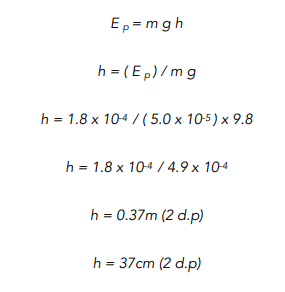
Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position in a gravitational field.
The equation for gravitational potential energy is GPE = mgh, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the object’s height above a reference level.
Gravitational potential energy is measured in joules (J).
The reference level used in the gravitational potential energy equation is usually the surface of the Earth.
The gravitational potential energy of an object is directly proportional to its height above a reference level.
The gravitational potential energy equation can be used to calculate the potential energy of an object at a certain height, to find the height of an object given its potential energy, or to calculate the change in potential energy of an object as it moves from one height to another.
The unit of measurement for mass in the gravitational potential energy equation is kilograms (kg).
The unit of measurement for height in the gravitational potential energy equation is meters (m).
The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.81 m/s^2.
Real-world examples of using the gravitational potential energy equation include calculating the potential energy of a roller coaster at the top of a hill, determining the height of a cliff based on the potential energy of a rock dropped from it, and calculating the change in potential energy of a water tower as it is filled and emptied.





Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment