Cell Division - Stem Cell Types (GCSE Biology)
Stem Cell Types
Growth
In order for organisms to grow and increase in size, their cells need to undergo:
- Differentiation. This process makes the cells specialised so they can carry out a specific function. This allows organisms to become more efficient.
- Cell division. The cells divide and increase in number by mitosis.
Plants also increase in size and grow by all of the above and:
- Elongation. The plant cell itself increases in size and lengthens which contributes to the plant’s growth. This usually happens at the tips of the roots and shoots of the plant.
Types of Stem Cells
A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell. This means that it has not yet specialised, and therefore has the ability to differentiate and form a specialised cell.
A stem cell can divide by mitosis to form a tissue of stem cells. Then different cell clusters can differentiate to different things, leading to many tissues of different specialised cells which is important for development, growth and repair. This is how the human body develops from a single embryonic stem cell.
Embryonic Stem Cells
- Stem cells in embryos are known as embryonic stem cells. Embryonic stem cells are found in early embryos and are completely undifferentiated. This means that they can be used to turn into any type of cell.
- Embryonic stem cells can be cloned and made into most types of cells. Environmental factors can be used to influence their differentiation into almost any type of cell. This has many potential medical applications.
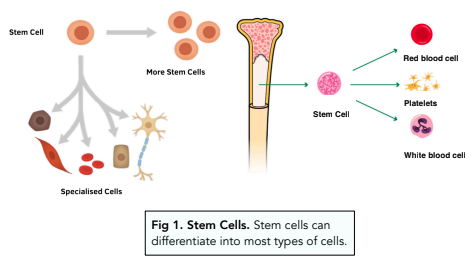
Adult Bone Marrow Stem Cells
- Stem cells in adults are only found in a few places. Stem cells can be found in the bone marrow, teeth and other areas. These cells cannot differentiate into any type of cells (like embryonic stem cells). Instead, they can only differentiate into a few predetermined cells, such as some blood cells.
- Adult stem cells can form many types blood cells. Adult stem cells can be used to form different blood cells, including red blood cells and white blood cells.
Plant Stem Cells
- Stem cells are found in plant meristems. Stem cells in plant meristems can differentiate to form any type of plant cell. They are present throughout the lifespan of the plant.
Cell division is the process by which a single cell divides into two or more daughter cells. This is a crucial process in the growth and reproduction of living organisms.
Stem cells are cells that have the ability to divide and differentiate into different types of cells. They play an important role in the growth and repair of tissues in the body.
The different types of stem cells include embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells are stem cells that are derived from embryos. They have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell in the body and are therefore considered to be pluripotent.
Adult stem cells are stem cells that are found in adult tissues. They have a more limited ability to differentiate into different types of cells, and are therefore considered to be multipotent.
Induced pluripotent stem cells are adult stem cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to have similar properties to embryonic stem cells. They have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell in the body and are therefore considered to be pluripotent.
The main difference between embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells is their ability to differentiate into different types of cells. Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent and have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell in the body, while adult stem cells are multipotent and have a more limited ability to differentiate.
Stem cells have significant potential for use in medical research and treatments. The ability of stem cells to differentiate into different types of cells makes them useful for studying the development of diseases and for developing new treatments.
The potential uses of stem cells in medicine include developing new treatments for diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders, and for regenerating damaged tissues and organs.
The challenges facing the use of stem cells in medicine include ethical concerns surrounding the use of embryonic stem cells, the need for further research to fully understand the properties and potential of stem cells, and the development of safe and effective methods for using stem cells in medical treatments.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment