Development and Understanding of Evolution - Evidence for Evolution: Resistant Bacteria (GCSE Biology)
Evidence for Evolution: Resistant Bacteria
Evidence for Evolution
Now, although creationist beliefs are still prevalent, the most commonly believed doctrine is that of Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection. This has occurred as more and most evidence supporting Darwin’s philosophy has been found.
The way that genes are passed onto offspring, with similar characteristics seen between generations of organisms is proof of natural selection. Usually the characteristics that provide a survival advantage are passed on.
Resistant Bacteria
The general understanding is that antibiotic resistance can be used to prove evolution.
- Bacteria reproduce at a high rate. Bacteria have an incredible ability to reproduce at a truly quick rate. This has allowed them to evolve rapidly, with whatever abilities were required.
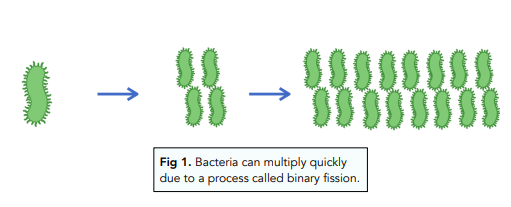
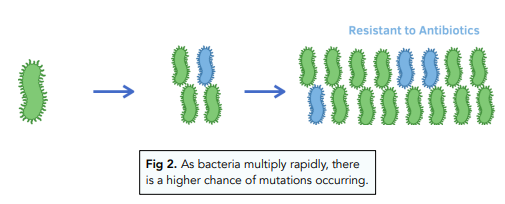
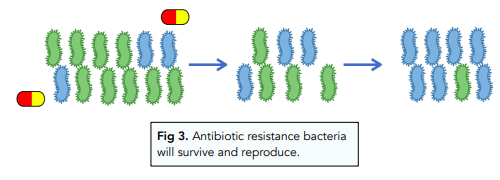
MRSA is an example of an antibiotic resistant strain of bacteria. The abbreviation stands for Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. This means that the bacteria are resistant to the antibiotic Methicillin, which is one of the stronger varieties. There are many methods fo reducing the rates of development of antibiotic resistant strains of bacteria. These include:
- The correct prescription of antibiotics. Antibiotics must only be prescribed when necessary. This means that they are not required in those with viral infections or non-serious infections. When prescribed when not necessary, there is an increased risk of mutation of bacteria, causing them to become resistant.
- The course of antibiotics must be completed. If the course of antibiotics is not completed, there is an increased risk that not all of the bacteria is eliminated. This can lead to more and more bacteria being present that can mutate and become resistant.
- A reduction in the use of agricultural antibiotics. Antibiotics are widely used in agriculture. Vancomycin, for example, is used often to promote growth in cattle, pigs and chicken. This use also can lead to an increase in antibiotic resistance as there is an increased chance of mutation occurring.
With all of this in mind, you may wonder, why not begin to develop new antibiotics. The reality is, this is very difficult and expensive.
Pharmaceutical companies stand to gain very little money from providing this service, as new antibiotics will not be used and will only be kept in storage, until all of the current antibiotics are out of use. Moreover, this research takes a lot of time and is superseded by the newer strains.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment