Meiosis - Mitosis and Meiosis (GCSE Biology)
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis
- Mitosis involves the formation of identical cells. Mitosis leads to the formation of two daughter cells that are identical to the original cell. They are known as diploid cells. It works via asexual reproduction. It is paramount in growth and repair, as you require many of the same types of cells.
- Mitosis is more common in some tissues than others. Mitosis is very prevalent in the skin and muscle cells.
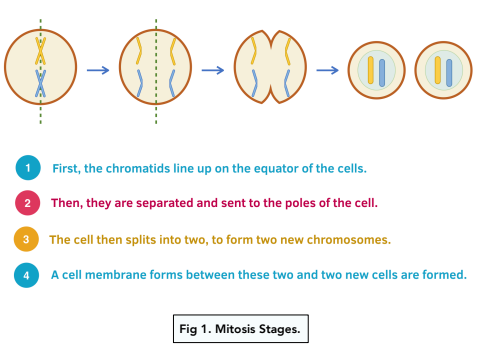
- Mitosis is a stage in the cell cycle. Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which the amount of genetic material doubles. First, the chromatids line up on the equator of the cells. Then, they are separated and sent to the poles of the cell. The cell then splits into two, to form two new chromosomes. A cell membrane forms between these two and two new cells are formed, both identical to the original parent cell.
Meiosis and Fertilisation
Meiosis is the method required for sexual reproduction. It does not occur in all cells and is mainly required for the formation of gametes.
- Meiosis makes gametes. Gametes are the sex cells of organisms. In animals, they are the sperm and egg cells, however in plants, they are pollen and egg cells. Gametes are an important product of meiosis.
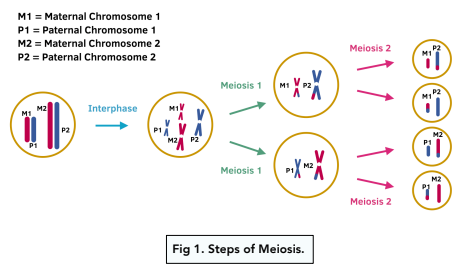
- During meiosis, the number of cells halves. In meiosis, the original cell divides twice, forming four daughter cells. Only one set of chromosomes is given to each daughter cell. This means that the cell is haploid. These cells formed are the gamete cells. As they only contain one set of chromosomes each, they will be genetically different from one another.
- Meiosis produces 4 haploid daughter cells. Whereas mitosis produced 2 identical diploid daughter cells, meiosis produces 4 non- identical haploid daughter cells. Therefore during fertilisation, when the egg and sperm fuse, two haploid cells join to form one diploid cell. In the final diploid cell, half the chromosomes come from the egg (mother) and half from the sperm (father).
- Fertilisation involves the fusion of gametes. The gametes each have half of the original numbers of chromosomes. This means that to form an embryo, the number of chromosome has to double and be back to the original number, which in humans is 46. This requires two gametes to fuse together.
- Fertilisation in humans requires the fusion of a sperm and an egg cell. The sperm and egg cells are the human gametes. Each contains 23 chromosomes. Therefore, they must fuse together to form a cell with 46 chromosomes. This leads to diversity, as the embryo will have characteristics from both the mother and the father. This cell is known as a zygote.
- Over time, the zygote forms an embryo. Over time, the zygote turns into an embryo. The embryo’s cells then divide by mitosis. Once the embryo is large enough, chemical signals trigger the specialisation of cells by differentiation. Examples of these signals include the Sonic Hedgehog signal.
Mitosis is the process by which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It is the type of cell division that occurs during growth and tissue repair.
Meiosis is the type of cell division that occurs in sexual reproduction. It results in the production of four genetically unique daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The steps of mitosis are:
Prophase: The chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the spindle apparatus forms.
Metaphase: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
Anaphase: The chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase: A new nucleus forms around each set of chromosomes and the cell splits in two.
Cytokinesis: The cytoplasm divides, creating two separate daughter cells.
The steps of meiosis are:
Prophase I: The chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the spindle apparatus forms.
Metaphase I: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
Anaphase I: The chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase I: A new nucleus forms around each set of chromosomes and the cell splits in two.
Cytokinesis I: The cytoplasm divides, creating two separate daughter cells.
Prophase II: The chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the spindle apparatus forms.
Metaphase II: The chromosomes align at the center of the cell.
Anaphase II: The chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase II: A new nucleus forms around each set of chromosomes and the cell splits in two.
Cytokinesis II: The cytoplasm divides, creating four separate daughter cells.
Mitosis results in the production of two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis results in the production of four genetically unique daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Meiosis is important in sexual reproduction because it allows for the shuffling of genetic information from two parents, resulting in offspring that are genetically diverse. This diversity can increase the chances of survival and adaptation in changing environments.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment