Variation - Cloning (GCSE Biology)
Cloning
Methods of Plant Cloning
1) Tissue Culture
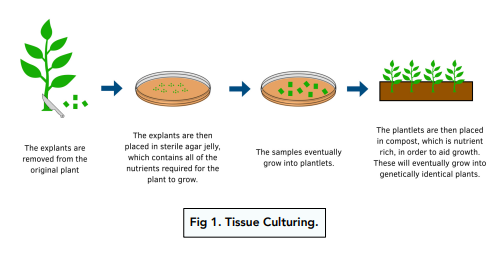
Tissue culture also known as micropropagation is a method of cloning plants, which involves growing new, genetically identical plants from parts of a parent plant. These parts are called explants. This is useful as it can be used to produce commercial quantities of genetically identical plants with desirable characteristics.
There are many steps in tissue culture:
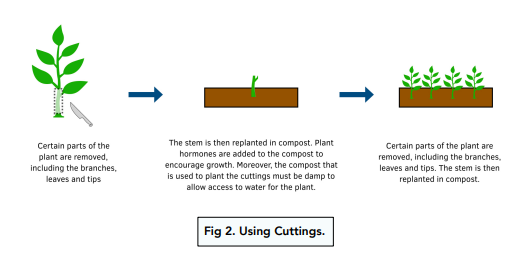
2) Cuttings
Using cuttings is an older, easier method of producing plants from a parent plant. It is often done by gardeners and does not require a sterile agar medium.
Methods of Animal Cloning
1) Animal Tissue Culture
Animal tissue culture has a similar process to plant tissue culture. A sample of tissue is extracted then its cells are separated with the help of enzymes. These cells are cultured and grown with the help of a growth medium which creates a suitable environment. These cells replicate and can be divided again into different vessels to grow even more. These cells can then be used in medical research for example, you can explore the effects of different substances on the tissue without causing complications in the whole body.
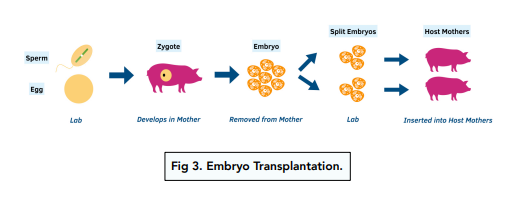
2) Embryo Transplantation
Embryo transplantation produces genetically identical offspring and is done via transplanting embryos to numerous hosts. It is quite a common process.
The steps of embryo transplantation:
- Fertilisation – sperm is taken from one animal, an egg is taken from another.
- Artificial Insemination – an animal is then artificially inseminated.
- Development of Embryos – the zygotes are allowed to develop into embryos.
- Removal of Embryos – embryos are then removed from the uterus of the inseminated animal.
- Splitting of Embryos – these embryos are split apart to form smaller cells. This process must take place before specialisation (when cells develop into different types of cells).
- Transplant into Host Mothers – you then transplant all of these embryos into host mothers. These embryos will all be genetically identical to one another and so will be clones.
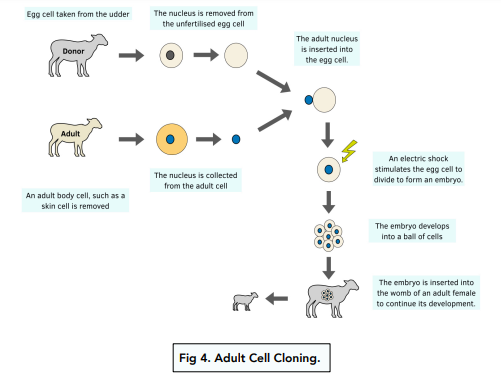
3) Adult Cell Cloning
In adult cell cloning, an adult cell’s nucleus is used to replace the nucleus in an egg cell.
Adult cell cloning has been around for around 20 years now. The first ever mammal was cloned in Edinburgh in 1996, and this was Dolly the Sheep. The process for adult cell cloning to produce Dolly is shown below:
Advantages of Adult Cell Cloning
- Produces animals with desired characteristics – cloning can produce animals that are transgenic and primed to produce required proteins for the body. As clones are produced, they will have the exact genetic information as the parent cell, so the required characteristics can easily be chosen. Hence, they can be used to produce human proteins. For example, cows and sheep can produce milk containing useful human proteins, chickens can produce proteins in their egg whites and antibodies for illnesses like arthritis can also be produced through this method.
- Helps prevent extinction – Another lesser known positive is the fact that it can be used to save animals from extinction. Endangered species can be cloned, in order to increase the population and then can breed to continue growing animals.
Disadvantages of Adult Cell Cloning
- Difficult process – adult cell cloning is a difficult process and requires lots of intense effort.
- Reduction in genetic variation – as genetically identical organisms are produced, there is an increased risk of reducing the genetic variation. This will reduce the size of the gene pool and lead to an increase in the incidence of genetic diseases.
- Ethical issues – there are ethical queries. Are humans playing God by cloning? Will the cloning of animals finally transition into the cloning of humans?
Variation refers to the differences that exist among individuals of the same species. This can include differences in physical characteristics, such as height or eye color, or differences in genetic information.
Cloning is the process of producing identical copies of an organism, or a group of cells, through asexual reproduction. This can be accomplished through several methods, including the use of stem cells or the duplication of genetic material.
There are several different types of cloning, including:
Reproductive cloning: This involves creating an exact genetic copy of an organism through the transfer of genetic material into an egg cell.
Therapeutic cloning: This involves creating an identical copy of a specific group of cells, such as stem cells, for medical purposes.
Gene cloning: This involves copying a specific gene for research or therapeutic purposes.
The benefits of cloning in biology include:
Studying the genetics of organisms and the role of specific genes in development and disease.
Creating new treatments for diseases by producing identical copies of cells with specific genetic information.
Preserving endangered species by producing identical copies through cloning.
The drawbacks of cloning in biology include:
The potential for ethical concerns, such as the creation of genetically identical individuals with identical experiences and personalities.
The risk of genetic abnormalities and health problems, as the genetic material used for cloning may not be perfect.
The cost and technical difficulties associated with the cloning process, which can limit its widespread use.
Cloning can impact genetic variation by producing identical copies of an organism or a group of cells. This can reduce the amount of genetic diversity within a species, as all of the individuals produced through cloning will be genetically identical.
Genetic variation is important in biology because it provides the raw material for evolution and adaptation to changing environments. The presence of genetic variation within a species allows for the survival of individuals with beneficial traits, which can be passed on to future generations. Without genetic variation, species may become less adaptable and more vulnerable to extinction.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment