Antibiotics - Monoclonal Antibodies in Pregnancy Tests (GCSE Biology)
Monoclonal Antibodies in Pregnancy Tests
Uses of Monoclonal Antibodies
Pregnancy Testing
Monoclonal antibodies can be used to detect particular antigens in patient samples of blood or tissue. For example, pregnancy testing uses monoclonal antibodies to detect for human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG). If a woman is pregnant, hCG will be found in urine, so we can do urine tests using monoclonal antibodies.
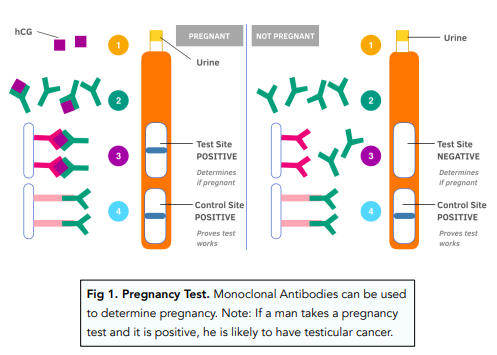
We can use fluorescent dyes when doing tests with monoclonal antibodies. We can evoke colour changes to help us detect positive tests. Refer to the diagram below to understand the following steps:
1. The person urinates. The person gives a urine sample. If they are pregnant, their urine should contain hCG.
2. Reaction Site. If hCG is present, it will bind to the free antibody, which has an enzyme attached to it.
3. Test Site. hCG bound to the free antibody (and by extension the dye enzyme) enters the test site. Here, the hCG-free antibody complex will bind to another fixed antibody using the hCG. This will bring the enzyme (attached to the complex) close to a dye substrate – a reaction occurs, causing a colour change.
4. Control site. There is fixed antibody in the control site. This will bind to any free antibody (not bound to hCG), and cause a colour change here.
If a person is not pregnant, the free antibody moves through the test site, and instead binds to the fixed antibody in the control site, causing a colour change here.
If a person is pregnant, the hCG-free antibody complex will form in the reaction site, and this complex binds in the test site, causing a colour change here. Some free antibody will still pass to the control site, so you will see two stripes.
Monoclonal Antibodies are laboratory-made copies of natural antibodies that are used to treat certain diseases.
Monoclonal Antibodies work by attaching to specific proteins on the surface of harmful cells, such as viruses, and neutralizing them.
Monoclonal Antibodies are used in pregnancy tests to detect the presence of a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a woman’s urine. If hCG is present, it means she is pregnant.
Monoclonal Antibodies in pregnancy tests are highly reliable and accurate when used correctly. They are able to detect pregnancy even in its early stages.
There are no known side effects or risks associated with using Monoclonal Antibodies in pregnancy tests. They are considered safe for use by pregnant women.
Monoclonal Antibodies are different from traditional antibiotics in that they target specific proteins on harmful cells, rather than killing bacteria. Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections, while Monoclonal Antibodies are used to treat certain diseases caused by viruses or other harmful cells.
Yes, Monoclonal Antibodies are also used to treat diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases caused by viruses.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment