Types of Diseases - Fungal and Protist Diseases (GCSE Biology)
Fungal and Protist Diseases
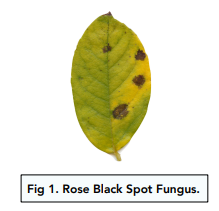
Rose Black Spot
- Rose black spot is a fungal infection. Rose black spot infects plants such as roses. It attacks the leaves, giving them black or purple spots. The leaves then turn yellow and fall off. This reduces the plants capability for photosynthesis, thus stunting its growth.
- Rose black spot is spread in the environment. Rose black spot has waterborne, airborne and direct transmission. It can be spread through water (e.g. rivers and lakes) or through wind.
- Rose black spot can be treated. Rose black spot is treated by fungicides and the removal of the infected leaves.
Chalara ash dieback
- Chalara ash dieback is a fungal infection. It infects ash trees causing leaf loss and bark lesions which are wounds.
- Chalara ash dieback is spread through the air. It is spread via the wind and also when ash trees that are infected are moved between different places.
- The spread of Chalara ash dieback can be prevented. If young ash trees that are infected are removed and replaced with a different species, the spread of this disease can be reduced. Moreover, the
movement or import of these tress can be restricted.
Barley powdery mildew
- Barley powdery mildew is a fungal infection that affects barley plants. It is caused by the fungus Erysiphe graminis.
- Barley powdery mildew affects photosynthesis. It makes fluffy white patches on the plant’s leaves thus, reducing photosynthesis and growth of the plant. This reduces the crop’s yields.
- Barley powdery mildew is spread in the air. The wind carries the spores and spreads the fungus between plants.
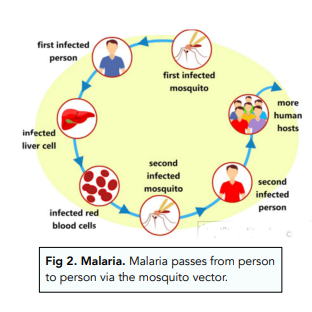
Malaria
- Malaria is caused by protists. Malaria is caused by the Plasmodium protist. This protist uses the mosquito as a vector.
- Malaria is spread in the blood. When a mosquito infected with plasmodium bites a human and sucks its blood, the mosquito passes on plasmodium spores to the human blood. The spores travel in the blood to the liver, where the spores divide. This gives the human malaria. Another mosquito can bite the same individual, take in spores, and then pass the spores on to another human – this is transmission.
- Malaria has unpleasant symptoms. Malaria causes feverish symptoms, along with chills, sweats, headaches, diarrhoea and vomiting. These are often recurrent and can be fatal.
- The spread of malaria can be reduced. Controlling the mosquito population and stopping biting can reduce the spread of malaria. Mosquito nets and repellant can be used for this, and tourists often take malaria tablets when going to high-risk areas (especially in Africa). There is, however, no vaccine for malaria.
Fungal diseases are infections caused by fungi, which are tiny organisms that can live in soil, on plants, and in the human body. Examples of fungal diseases include athletes foot, ringworm, yeast infections, and Aspergillosis.
Protist diseases are infections caused by single-celled organisms known as protists. Some examples of protist diseases include malaria, which is caused by a parasite known as Plasmodium, and amoebiasis, which is caused by a parasite called Entamoeba histolytica.
Fungal diseases can spread through the air, through contact with infected soil or plants, or through contact with infected animals. Some fungal diseases can also spread through direct contact with infected people or through sexual contact.
Protist diseases can spread through the bite of infected insects, such as mosquitoes, through contaminated water or food, and through sexual contact in some cases.
The symptoms of fungal diseases can vary depending on the type of infection and the part of the body affected. Common symptoms of fungal diseases include skin rashes, itching, burning, redness, and swelling. In some cases, fungal diseases can also cause fever, fatigue, and difficulty breathing.
The symptoms of protist diseases can also vary depending on the type of infection and the part of the body affected. Common symptoms of protist diseases include fever, headache, muscle pain, and fatigue. In some cases, protist diseases can also cause vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
Fungal diseases are usually treated with antifungal medications, which can be taken orally or applied to the skin. In some cases, fungal diseases can be treated with topical creams or ointments. In severe cases, fungal diseases may require treatment with intravenous antifungal medications.
Protist diseases are usually treated with antiparasitic medications, which can be taken orally or intravenously. In some cases, protist diseases may also require treatment with antimalarial drugs.
Fungal and protist diseases can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, avoiding contaminated food and water, using insect repellent to prevent insect bites, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals. In some cases, vaccines may also be available to prevent certain protist diseases, such as malaria.






Still got a question? Leave a comment
Leave a comment